High-Purity Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution from Aure Chemical – Your Trusted Source
Palladium(II) nitrate solution, Pd(NO₃)₂ in aqueous form, CAS No. 10102-05-3, is a convenient, halide-free palladium(II) precursor widely used in modern materials processing and catalysis. Supplied by Aure Chemical as a clear to pale brown liquid with palladium concentrations typically ranging from 5–20% Pd (w/w), this stable solution offers excellent solubility and clean decomposition characteristics. It serves as an efficient Pd source for thin-film deposition (spin-coating, inkjet, dip-coating), wet impregnation of supported palladium catalysts, preparation of organometallic palladium complexes, and synthesis of Pd-containing functional materials for electronics, fuel cells, sensors, and advanced research. Its nitrate-based composition eliminates chloride contamination risks, making it ideal for high-purity applications in microelectronics and electrocatalysis. Aure Chemical provides precise Pd content control, low impurity profiles, and secure palladium sourcing to ensure reproducible results in industrial and laboratory settings worldwide.
Basic Information of Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution
Aure Chemical delivers Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution as a high-quality aqueous Pd(II) precursor optimized for deposition, impregnation, and synthesis applications, available in commercial Pd concentrations with verified composition.
| CAS No. | 10102-05-3 |
|---|
| EC No. | 233-265-8 |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Pd(NO3)2 (aq.) |
|---|
| Molecular Weight | 230.43 g/mol (anhydrous basis) |
|---|
| Appearance | Clear to pale brown liquid (aqueous solution, typically 5–20% Pd w/w) |
|---|
| Odor | Odorless to slight nitric |
|---|
| Melting point | Not applicable (liquid solution) |
|---|
| Boiling point | >100 °C (water-based; decomposes on heating) |
|---|
| Density | 1.05–1.35 g/mL at 25 °C (concentration-dependent) |
|---|
| Solubility | Miscible with water; soluble in alcohols, acetone, acetonitrile |
|---|
| Nature (hazards) | Oxidizing liquid, may intensify fire, causes skin and eye irritation, harmful if swallowed, toxic to aquatic life |
|---|
| RIDADR | UN 3099, Oxidizing liquid, corrosive, n.o.s. (Palladium(II) nitrate solution), Class 5.1 (8), Packing Group III |
|---|
| Chemical Structure | 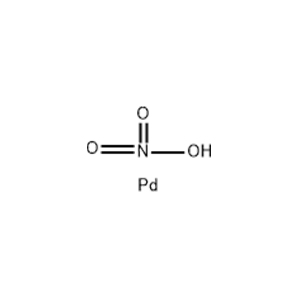 |
|---|
Aure Chemical offers customizable Pd concentrations (e.g., 5%, 10%, 15%, 20% Pd w/w), adjusted acidity, and specialized packaging to align perfectly with your deposition, catalyst, or synthesis process specifications.
Primary Applications of Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution
Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution provides a clean, ready-to-use Pd source for solution processing, enabling precise palladium incorporation in high-technology and catalytic applications. As a halide-free Pd(II) precursor, it is particularly suitable for systems requiring controlled coordination chemistry and uniform metal distribution, frequently utilized in workflows related to
palladium salts and catalyst precursor preparation.
Thin-Film Palladium Deposition
Ideal for spin-coating, dip-coating, or ink formulations to produce palladium electrodes, seed layers, or conductive films in microelectronics, sensors, and MEMS devices. Controlled thermal decomposition of nitrate complexes allows formation of uniform metallic palladium films with minimal halide contamination, critical for advanced electronic components.
Supported Palladium Catalyst Impregnation
Used in wet impregnation of carbon, alumina, silica, or other supports to create high-dispersion Pd catalysts for hydrogenation, hydrogenolysis, and cross-coupling reactions. Upon drying and controlled reduction, the nitrate-derived palladium species generate finely dispersed metallic Pd sites suitable for applications described under
hydrogenation and supported palladium catalysis.
CVD / ALD Precursor Solutions
Serves as a liquid delivery source or component in chemical vapor deposition and atomic layer deposition processes for uniform, high-purity palladium thin films. Its solubility and defined decomposition profile support reproducible film growth in semiconductor and sensor fabrication.
Organometallic Palladium Complex Synthesis
Acts as a halide-free Pd(II) precursor for preparing phosphine, carbene, or amine Pd complexes used in homogeneous catalysis and materials research. The absence of chloride facilitates cleaner ligand exchange reactions and controlled complex formation.
Fuel Cell & Electrocatalyst Development
Enables synthesis of Pd nanoparticles, Pd alloys, or Pd-modified carbon supports for fuel cells, electrolyzers, and energy conversion technologies. Nitrate-based systems allow controlled reduction to nanoscale palladium particles with tunable dispersion and morphology.
Advanced Materials & Nanotechnology
Facilitates controlled reduction to generate palladium nanostructures, functional coatings, or hydrogen-permeable membranes requiring high purity and controlled Pd loading. Such materials are critical in hydrogen separation, sensing, and catalytic microreactor technologies.
For a comprehensive overview of palladium material categories—including salts, oxides, supported catalysts, and organometallic systems across industrial sectors—refer to
Palladium Compounds: Applications, Categories & Industrial Uses.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for Your Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution Supply?
Aure Chemical supplies Palladium(II) Nitrate Solution with controlled concentration, analytical consistency, and technical support tailored for advanced deposition, catalytic, and materials applications.
Accurate & Consistent Pd Concentration
Precise analytical control ensures uniform palladium content, low impurities, and batch reproducibility for reliable deposition or catalytic performance in high-technology processes.
Halide-Free Formulation
Nitrate-based solution eliminates chloride contamination risks, making it suitable for electronics, fuel cells, and processes demanding ultra-high purity palladium.
Custom Solution Tailoring
Adjustable Pd levels, concentration ranges, and compatible solvent systems can be provided to align with specific deposition or catalyst preparation requirements.
Technical Process Support
Technical guidance is available for solution handling, impregnation techniques, thermal treatment, reduction protocols, and optimization of palladium dispersion.
Regulatory & Sustainability Focus
Full COA, REACH, RoHS, and SDS documentation are available, alongside precious metal recycling and recovery support to enhance sustainability and regulatory compliance.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Oxidizing Liquids (Category 2 or 3); Acute Toxicity, Oral (Category 4); Skin Corrosion/Irritation (Category 1B or 2); Serious Eye Damage (Category 1); Aquatic Chronic (Category 2 or 3)
Hazard Statements: H272: May intensify fire; oxidizer; H302: Harmful if swallowed; H314 or H315: Causes severe skin burns or irritation; H318: Causes serious eye damage; H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
UN Number: UN 3099
Hazard Class: 5.1 (Oxidizing substances) + 8 (Corrosive)
Packing Group: III
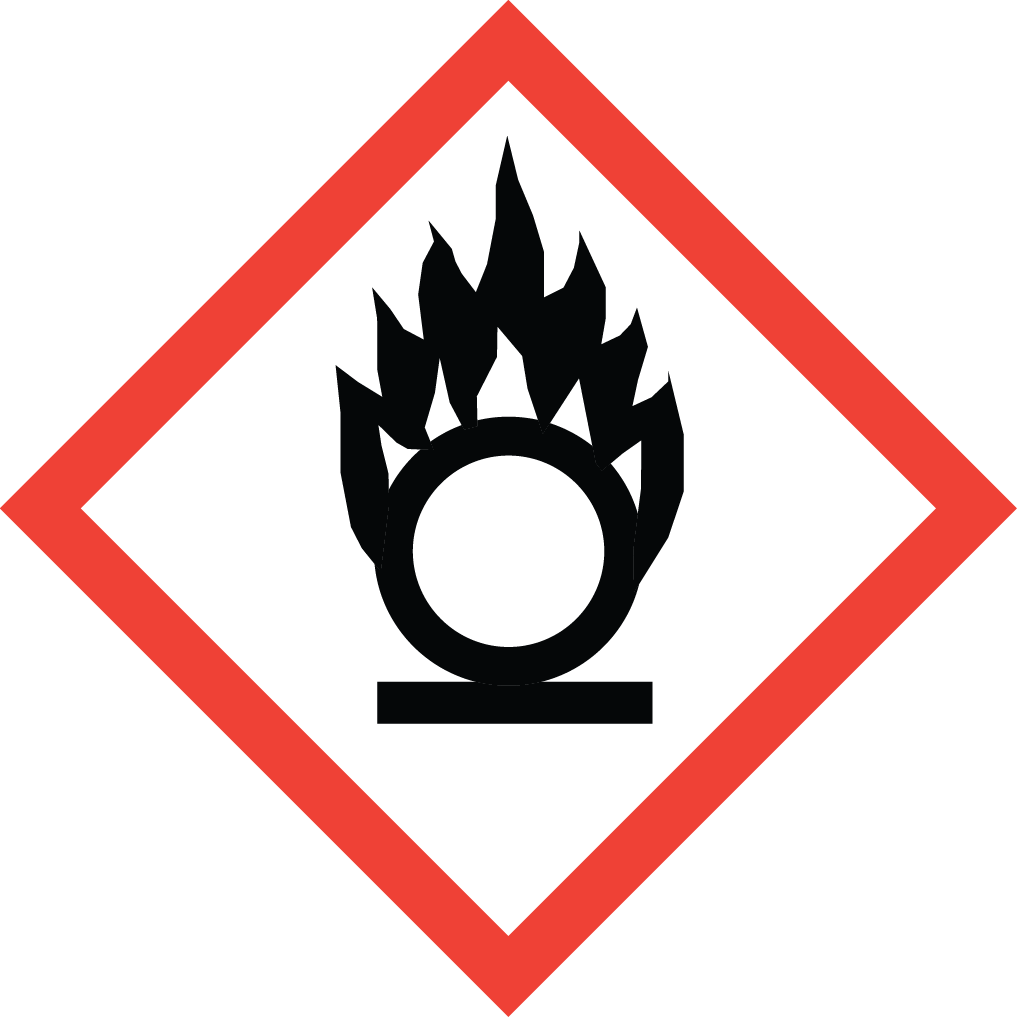 GHS03: Oxidizer
GHS03: Oxidizer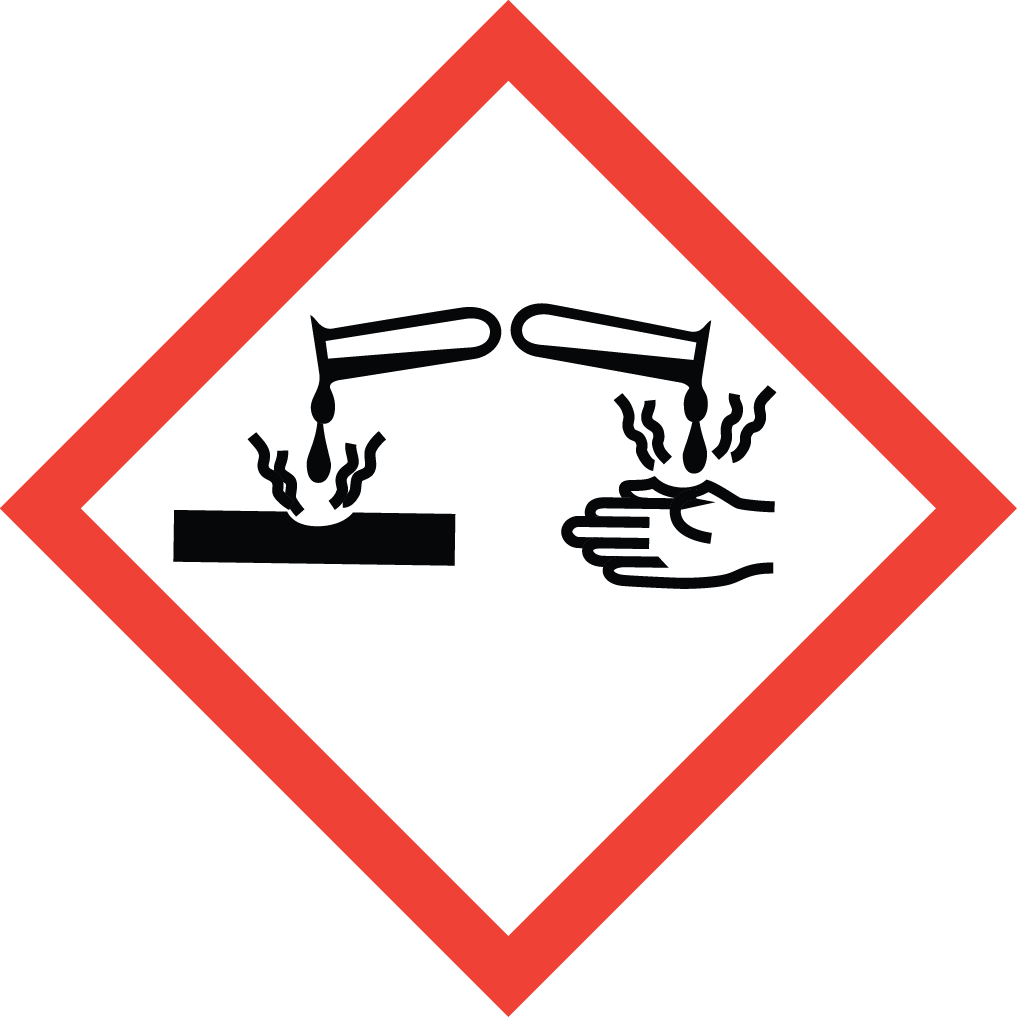 GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive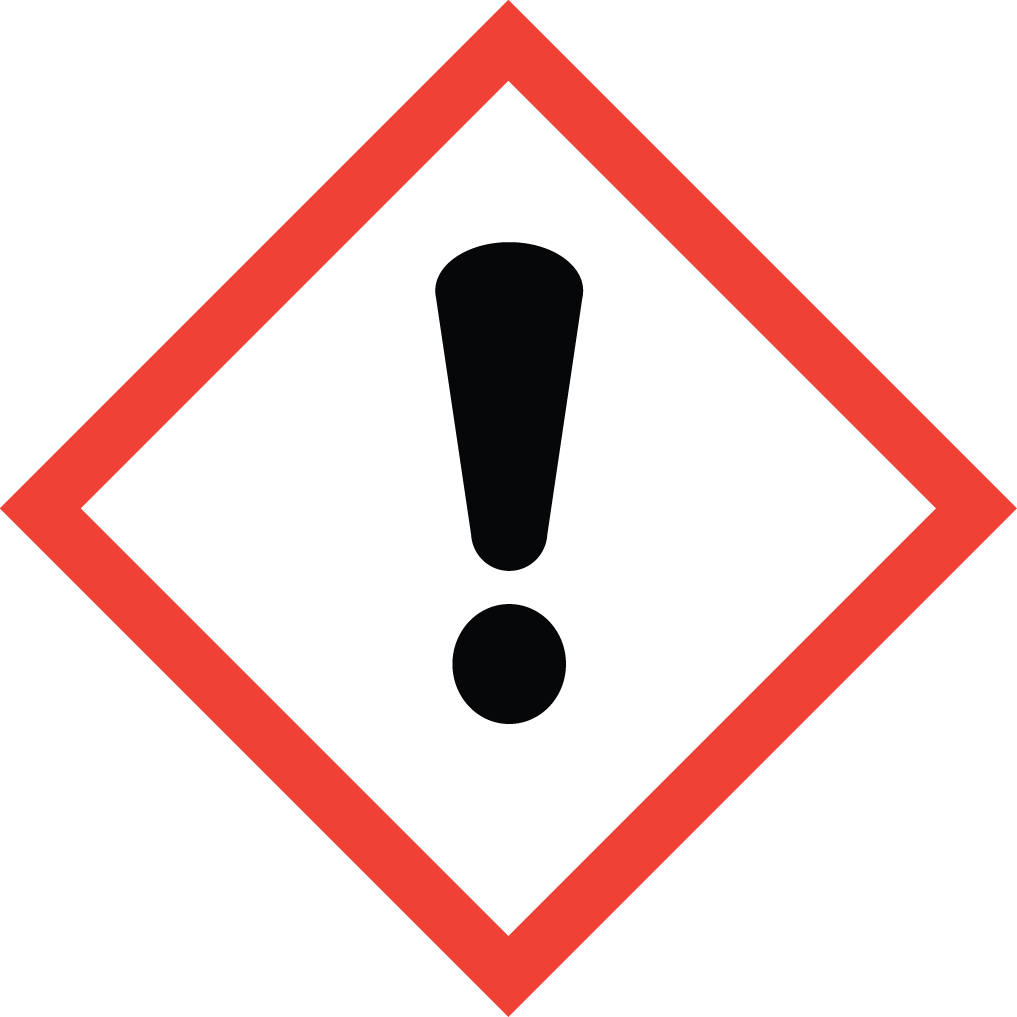 GHS07: Exclamation mark (irritant, acute toxicity)
GHS07: Exclamation mark (irritant, acute toxicity)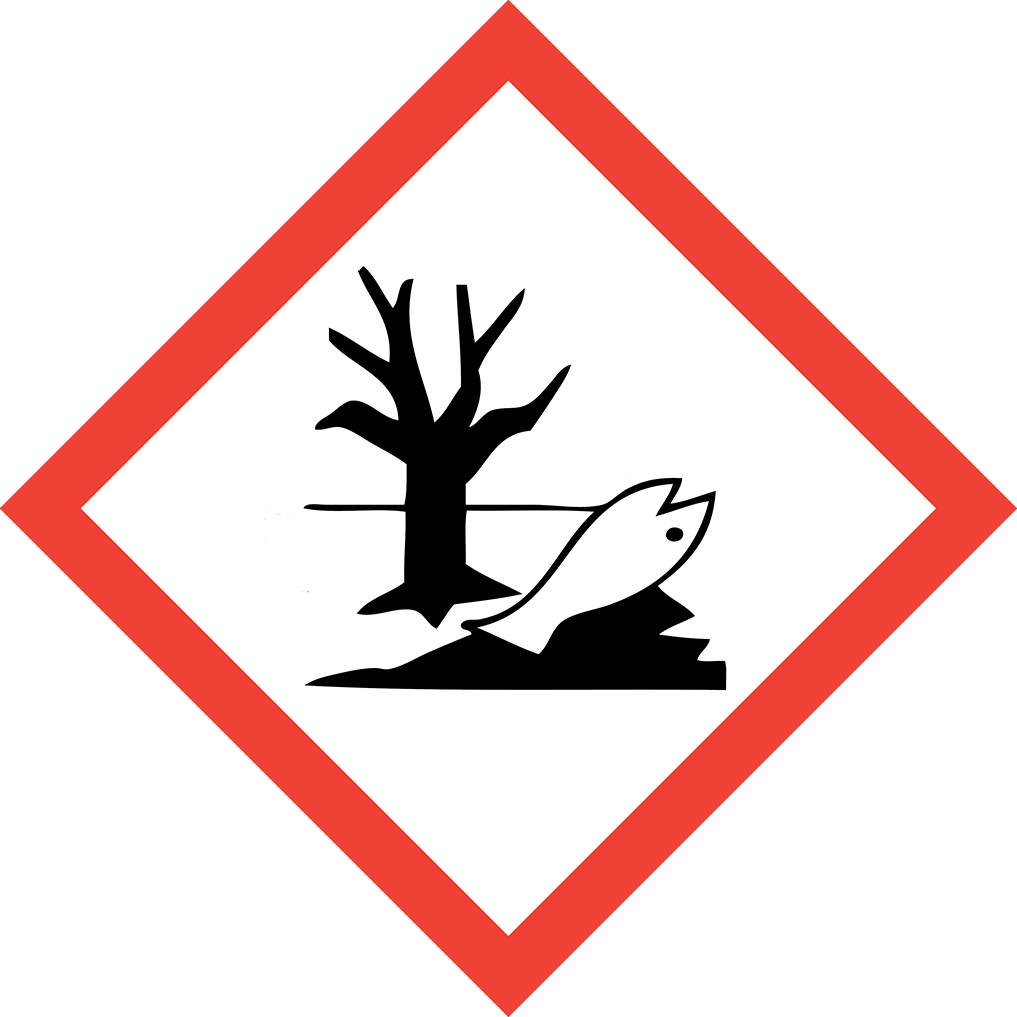 GHS09: Environment (aquatic toxicity)
GHS09: Environment (aquatic toxicity)
