High-Purity Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate from Aure Chemical – Your Trusted Source
Palladium(II) acetylacetonate, Pd(acac)₂ or bis(acetylacetonato)palladium(II), CAS No. 14024-61-4, is a highly regarded organometallic Pd(II) complex valued for its volatility, thermal stability, and clean decomposition behavior. Supplied by Aure Chemical as bright yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder with high palladium content (approximately 35–36% Pd), this air-stable, neutral compound exhibits excellent solubility in organic solvents and serves as a preferred precursor for chemical vapor deposition (CVD), atomic layer deposition (ALD), and solution-based thin-film processes. It is widely employed in depositing high-purity palladium films, preparing supported Pd catalysts, synthesizing organometallic complexes, and producing palladium nanoparticles or functional materials for electronics, fuel cells, sensors, and catalysis research. Aure Chemical delivers stringent purity control, low residual impurities, and secure palladium sourcing to ensure reproducible deposition and catalytic performance in advanced technology and R&D applications worldwide.
Basic Information of Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate
Aure Chemical provides Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate as a premium volatile Pd(II) precursor with verified palladium content and exceptional purity for thin-film and catalytic applications.
| CAS No. | 14024-61-4 |
|---|
| EC No. | 237-859-8 |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Pd(C5H7O2)2 |
|---|
| Molecular Weight | 304.58 g/mol |
|---|
| Appearance | Bright yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder |
|---|
| Odor | Odorless to slight characteristic |
|---|
| Melting point | 200–205 °C (decomposes) |
|---|
| Boiling point | Sublimes ~180–200 °C under vacuum |
|---|
| Density | approx. 1.8–2.0 g/cm³ |
|---|
| Solubility | Insoluble in water; soluble in chloroform, dichloromethane, toluene, benzene, acetone |
|---|
| Nature (hazards) | May cause skin and eye irritation, harmful if swallowed or inhaled, toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects |
|---|
| RIDADR | UN 3077, Environmentally hazardous substance, solid, n.o.s. (Palladium(II) acetylacetonate), Class 9, Packing Group III |
|---|
| Chemical Structure | 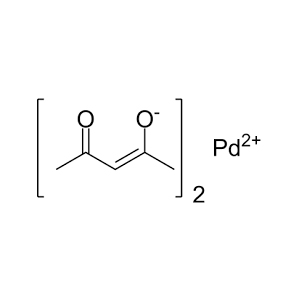 |
|---|
Aure Chemical offers customizable options including purity grades (99%+ Pd basis), controlled particle size, and inert-atmosphere packaging to meet CVD/ALD, catalyst, or synthesis process specifications.
Primary Applications of Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate
Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate excels as a volatile, halide-free Pd precursor for high-purity thin-film deposition and catalyst preparation in advanced technology sectors. As a β-diketonate complex, it exhibits favorable thermal stability and controlled volatility, making it particularly suitable for applications described under
advanced palladium organometallic catalysis and materials systems,
where clean ligand dissociation and residue-free metal formation are critical.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) & Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)
Serves as a standard precursor for depositing conformal, high-purity palladium thin films, electrodes, or catalytic layers in microelectronics, MEMS, and fuel cell applications. Controlled thermal decomposition of the acetylacetonate ligands enables uniform metallic palladium film formation with minimal halide contamination.
Supported Palladium Catalyst Preparation
Used in solution impregnation or gas-phase methods to produce highly dispersed Pd on carbon, alumina, or oxide supports for hydrogenation, hydrogenolysis, and cross-coupling catalysis. Ligand removal under reductive conditions generates finely distributed Pd nanoparticles with high catalytic surface area.
Palladium Nanoparticle & Nanostructure Synthesis
Enables controlled thermal or chemical reduction to generate Pd nanoparticles, nanowires, or clusters for sensors, fuel cells, and biomedical nanotechnology. The molecular structure of Pd(acac)₂ allows predictable nucleation behavior during nanoparticle growth.
Organometallic Complex & Materials Research
Acts as a Pd(II) source for synthesizing mixed-ligand complexes, luminescent Pd compounds, or functional organometallics in academic and industrial R&D. The acetylacetonate ligands can be partially or fully displaced to form customized coordination complexes.
Electrocatalyst Development for Energy Applications
Facilitates preparation of Pd-based catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), alcohol oxidation, and other processes in fuel cells and electrolyzers. Controlled decomposition supports uniform Pd dispersion on conductive supports.
Thin-Film Electrodes & Sensors
Supports deposition of Pd microelectrodes, catalytic surfaces, or gas-sensitive layers in chemical sensors, biosensors, and electrochemical devices. Film thickness and morphology can be precisely tuned through deposition parameter control.
For a comprehensive overview of palladium material categories—including salts, oxides, supported catalysts, and organometallic systems across industrial applications—refer to
Palladium Compounds: Applications, Categories & Industrial Uses.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for Your Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate Supply?
Select Aure Chemical as your strategic partner for Palladium(II) Acetylacetonate, delivering premium volatility, technical support, and stable palladium supply for cutting-edge applications.
High Purity & Volatile Consistency
Rigorous quality control ensures uniform Pd content, low impurities, and reproducible sublimation/decomposition behavior for reliable thin-film deposition.
Secure Precious Metal Sourcing
Transparent, responsible palladium procurement with inventory strategies to provide supply stability and competitive pricing.
Technical Deposition Expertise
Dedicated specialists offer guidance on precursor handling, CVD/ALD parameters, reduction protocols, and process optimization.
Comprehensive Regulatory Compliance
Full COA, REACH, RoHS, and detailed SDS documentation to facilitate integration into global electronics and catalysis operations.
Sustainability Focus
Ethical sourcing practices and palladium recovery/recycling programs aligned with ESG requirements and sustainable materials development.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Acute Toxicity, Oral (Category 4); Skin Irritation (Category 2); Eye Irritation (Category 2A); Specific Target Organ Toxicity, Single Exposure (respiratory) (Category 3); Aquatic Chronic (Category 2)
Hazard Statements: H302: Harmful if swallowed; H315: Causes skin irritation; H319: Causes serious eye irritation; H335: May cause respiratory irritation; H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
UN Number: UN 3077
Hazard Class: 9 (Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles)
Packing Group: III
 GHS07: Exclamation mark (irritant, acute toxicity)
GHS07: Exclamation mark (irritant, acute toxicity) GHS09: Environment (aquatic toxicity)
GHS09: Environment (aquatic toxicity)
