High-Purity Palladium(II) Chloride from Aure Chemical – Your Trusted Source
Palladium(II) chloride, PdCl₂, CAS No. 7647-10-1, is a fundamental anhydrous palladium(II) compound serving as one of the most versatile precursors in palladium chemistry. Supplied by Aure Chemical as a dark red to reddish-brown crystalline powder with high palladium content (approximately 59–60% Pd), this hygroscopic solid is highly reactive toward coordinating ligands and commonly used to generate active Pd(II) or Pd(0) species in solution. It is the preferred starting material for preparing palladium precatalysts employed in cross-coupling reactions (Suzuki, Heck, Sonogashira, Negishi), C–H activation, carbonylation, and allylic substitution, as well as for synthesizing organometallic complexes, thin-film deposition sources, and supported palladium catalysts. Its well-defined reactivity and purity make it indispensable in pharmaceutical API synthesis, fine chemicals, electronics, and advanced materials research. Aure Chemical ensures precise Pd assay, low impurity levels, and secure palladium sourcing to deliver reproducible performance for laboratory and industrial applications worldwide.
Basic Information of Palladium(II) Chloride
Aure Chemical offers Palladium(II) Chloride as a premium-grade anhydrous Pd(II) precursor with verified palladium content and exceptional purity for catalytic and synthetic applications.
| CAS No. | 7647-10-1 |
|---|
| EC No. | 231-596-2 |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | PdCl2 |
|---|
| Molecular Weight | 177.33 g/mol |
|---|
| Appearance | Dark red to reddish-brown crystalline powder |
|---|
| Odor | Odorless |
|---|
| Melting point | 678–680 °C (decomposes) |
|---|
| Boiling point | Not applicable (decomposes) |
|---|
| Density | approx. 4.09 g/cm³ |
|---|
| Solubility | Insoluble in water (slowly hydrolyzes); soluble in hydrochloric acid, acetonitrile, DMF, DMSO (forms complexes) |
|---|
| Nature (hazards) | Causes severe skin burns and eye damage, may cause allergic skin reaction, harmful if swallowed, toxic to aquatic life |
|---|
| RIDADR | UN 3260, Corrosive solid, acidic, inorganic, n.o.s. (Palladium dichloride), Class 8, Packing Group III |
|---|
| Chemical Structure | 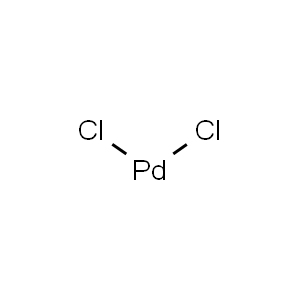 |
|---|
Aure Chemical provides customizable options including purity grades (99%+ Pd basis), moisture-protected packaging, and specific batch sizes to accommodate your catalyst preparation, synthesis, or deposition requirements.
Primary Applications of Palladium(II) Chloride
Palladium(II) Chloride serves as a versatile Pd(II) precursor, readily forming soluble coordination complexes in polar media such as hydrochloric acid or acetonitrile, which subsequently generate active catalytic species in numerous palladium-mediated transformations. Due to its well-defined coordination chemistry and predictable reduction behavior, it is widely utilized in systems associated with
palladium salts and catalyst precursor preparation,
where controlled conversion to catalytically active Pd(0) species is required.
Cross-Coupling Catalyst Preparation
Acts as the primary Pd source for generating precatalysts used in Suzuki-Miyaura, Heck, Sonogashira, Stille, and Negishi couplings, enabling efficient C–C bond formation in pharmaceutical and fine chemical synthesis. In situ reduction of PdCl₂ in the presence of ligands or reducing agents produces active Pd(0) complexes suitable for scalable catalytic systems.
C–H Activation & Functionalization
Facilitates direct C–H arylation, halogenation, and olefination reactions, providing atom-economical access to complex molecules with reduced prefunctionalization steps. The chloride coordination sphere can influence catalytic pathways and stabilize key Pd(II) intermediates in directed C–H activation processes.
Allylic Substitution & Tsuji-Trost Reactions
Serves as a Pd source for allylic alkylation, amination, and etherification, offering high regio- and stereocontrol in the synthesis of natural products and advanced intermediates. In these reactions, PdCl₂ is typically converted into π-allyl palladium complexes that govern nucleophilic substitution selectivity.
Carbonylation & CO-Coupling Reactions
Enables carbonylative couplings, esterifications, and amidations, providing efficient routes to carboxylic acid derivatives and heterocycles in specialty chemicals. Under CO atmosphere, palladium chloride-based systems form acyl-palladium intermediates, supporting industrial-scale carbonylation chemistry.
Thin-Film & CVD Palladium Deposition
Used in solution-based or vapor-phase processes to deposit high-purity palladium films, electrodes, or seed layers in microelectronics and sensor applications. Its defined stoichiometry and controlled decomposition characteristics make it suitable for materials science and surface engineering applications.
Organometallic Complex & Catalyst Development
Employed as starting material for synthesizing Pd(II) and Pd(0) complexes, ligands, and novel catalytic systems in academic and industrial R&D. Its reactivity toward phosphines, amines, and N-heterocyclic carbene ligands enables systematic catalyst design and screening studies.
For a broader classification of palladium materials, including salts, oxides, supported catalysts, and organometallic complexes across industrial sectors, refer to
Palladium Compounds: Applications, Categories & Industrial Uses.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for Your Palladium(II) Chloride Supply?
Partner with Aure Chemical for Palladium(II) Chloride to access premium quality, technical expertise, and secure palladium supply tailored to your catalytic and synthetic needs.
High Palladium Content Consistency
Rigorous analytical verification ensures accurate Pd assay, low residual impurities, and batch-to-batch reproducibility for dependable downstream performance.
Secure Palladium Sourcing
Transparent, responsible procurement with inventory buffering to provide supply stability and competitive pricing amid market fluctuations.
Technical Application Guidance
Dedicated specialists offer advice on dissolution, complex formation, catalyst activation, and reaction optimization for your specific processes.
Full Regulatory Compliance
Comprehensive documentation including Certificates of Analysis, REACH, RoHS, and detailed SDS to streamline global operations and audits.
Sustainability & Recycling Support
Ethical sourcing practices and palladium recovery/recycling programs aligned with ESG objectives and circular economy principles.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Skin Corrosion/Irritation (Category 1B); Serious Eye Damage (Category 1); Skin Sensitization (Category 1); Acute Toxicity, Oral (Category 4); Aquatic Chronic (Category 2)
Hazard Statements: H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage; H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction; H302: Harmful if swallowed; H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects
UN Number: UN 3260
Hazard Class: 8 (Corrosive substances)
Packing Group: III
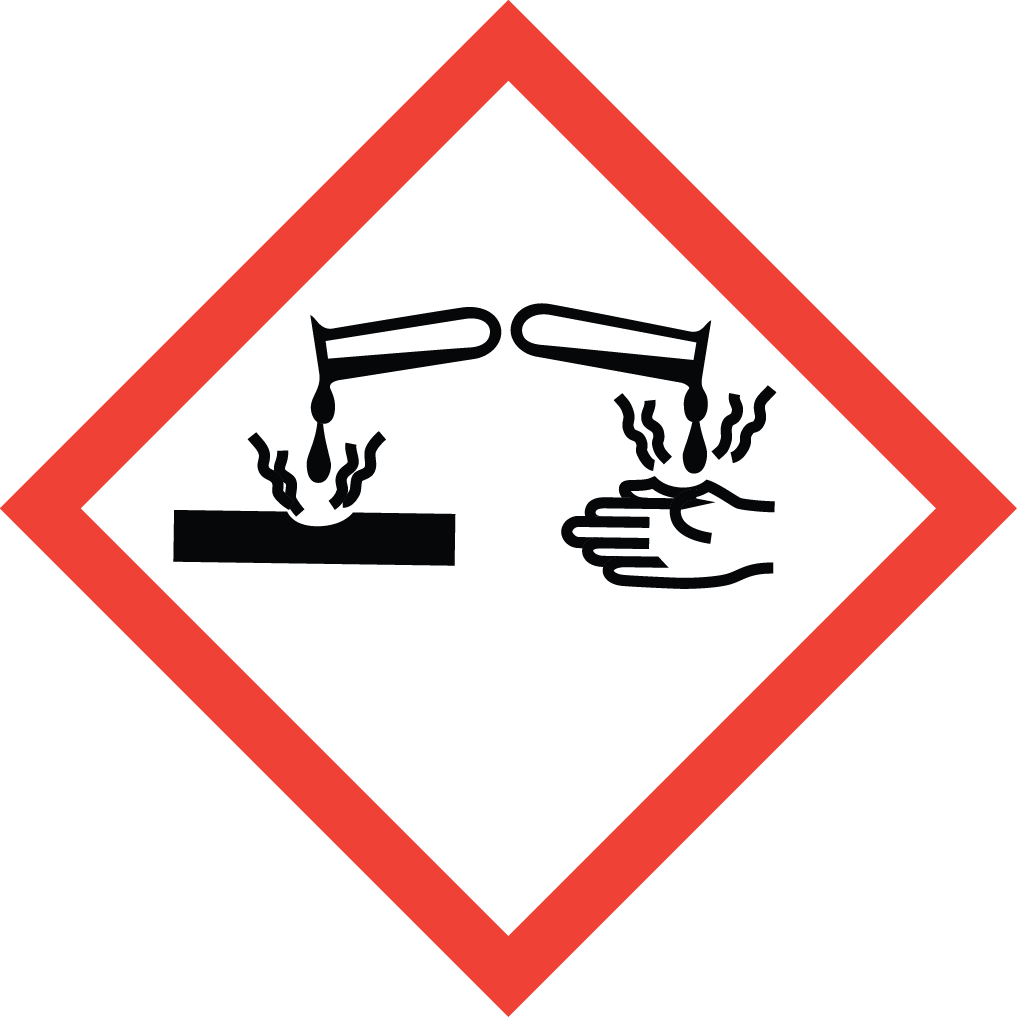 GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive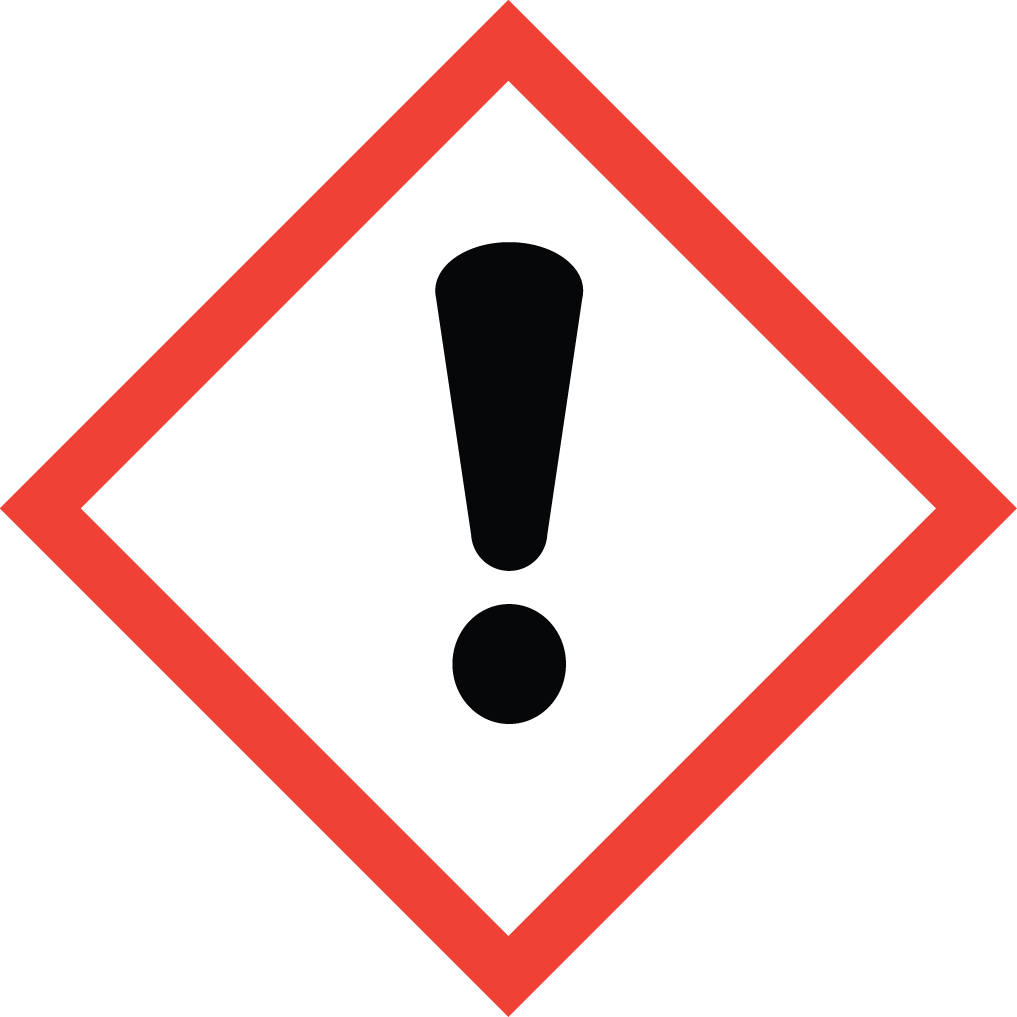 GHS07: Exclamation mark (sensitizer, acute toxicity)
GHS07: Exclamation mark (sensitizer, acute toxicity)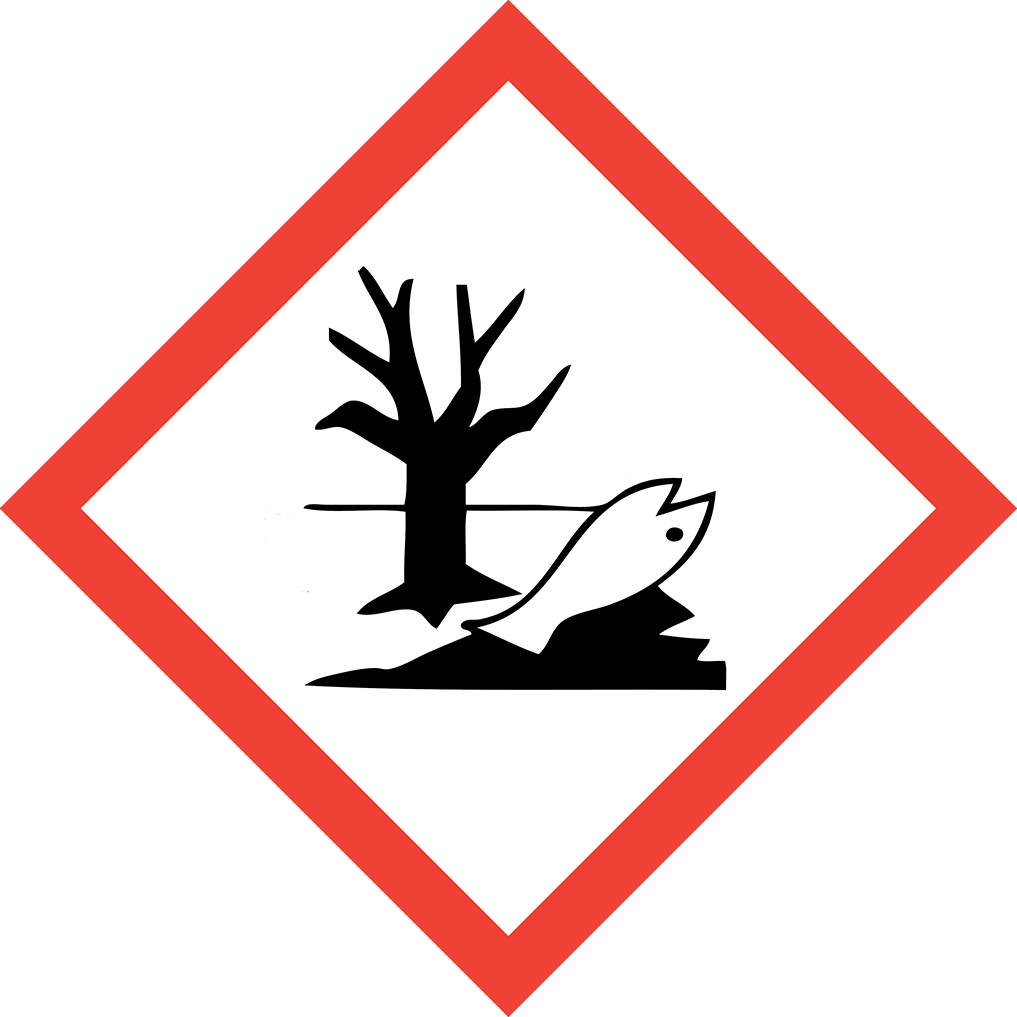 GHS09: Environment (aquatic toxicity)
GHS09: Environment (aquatic toxicity)
