High-Purity Palladium(II) Hydroxide from Aure Chemical – Your Trusted Source
Palladium(II) hydroxide, Pd(OH)₂, CAS No. 12135-22-7, is a key palladium(II) precursor widely employed in the preparation of heterogeneous palladium catalysts and organometallic compounds. Supplied by Aure Chemical as a dark brown to black moist powder or hydrated solid with high palladium content (approximately 70–75% Pd), this material is readily reduced to active Pd(0) or used directly in oxidation processes. It offers excellent reactivity for generating supported Pd catalysts on carbon, alumina, or silica, enabling efficient hydrogenation, hydrogenolysis, and selective oxidation reactions in pharmaceutical intermediates, fine chemicals, and specialty materials. Its controlled hydration and purity minimize variability in catalyst performance, making it a preferred choice for industrial impregnation and reduction steps. Aure Chemical provides consistent composition, low chloride/impurity levels, and secure palladium sourcing to ensure reproducible activity and longevity in demanding catalytic applications worldwide.
Basic Information of Palladium(II) Hydroxide
Aure Chemical supplies Palladium(II) Hydroxide as a premium Pd(II) precursor with verified high palladium content and controlled hydration for catalyst and synthesis applications.
| CAS No. | 12135-22-7 |
|---|
| EC No. | 235-219-6 |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | Pd(OH)2 |
|---|
| Molecular Weight | 140.43 g/mol |
|---|
| Appearance | Dark brown to black moist powder or hydrated solid |
|---|
| Odor | Odorless |
|---|
| Melting point | Decomposes before melting (>100 °C) |
|---|
| Boiling point | Not applicable (decomposes) |
|---|
| Density | approx. 3.5–4.0 g/cm³ (dry basis) |
|---|
| Solubility | Insoluble in water; soluble in acids (e.g., HCl, HNO₃) with decomposition |
|---|
| Nature (hazards) | May cause respiratory irritation, skin and eye irritation, harmful if inhaled as dust, toxic to aquatic life |
|---|
| RIDADR | Not regulated (non-hazardous for transport under standard classifications; consult SDS for specific handling) |
|---|
| Chemical Structure | 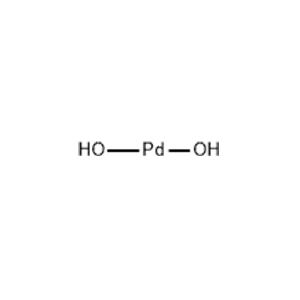 |
|---|
Aure Chemical offers customizable options including palladium content specification, moisture level control, particle size distribution, and supported forms to align with your catalyst preparation or process requirements.
Primary Applications of Palladium(II) Hydroxide
Palladium(II) Hydroxide functions as a reactive Pd(II) source, readily convertible under thermal or reductive conditions to active Pd(0) or PdO species for efficient catalytic transformations in fine chemicals and materials processing. Owing to its high surface reactivity and ease of reduction, it is widely employed in systems associated with
hydrogenation and supported palladium catalysis,
where controlled activation and heterogeneous stability are essential.
Supported Palladium Catalyst Preparation
Serves as the preferred precursor for impregnating or precipitating high-dispersion Pd on carbon, alumina, silica, or other carriers, yielding robust hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis catalysts. Controlled precipitation and reduction steps enable uniform metal dispersion and optimized catalytic surface area.
Hydrogenation & Hydrogenolysis
Reduced in situ to Pd(0) for selective reduction of alkenes, alkynes, nitro groups, and debenzylation of protecting groups in pharmaceutical and agrochemical synthesis. The heterogeneous nature of Pd(OH)₂-derived systems allows straightforward catalyst separation and reuse in multi-step industrial workflows.
Selective Oxidation Reactions
Used directly or as a PdO precursor for alcohol oxidation to aldehydes/ketones and other oxidative transformations using air or oxygen in fine chemical production. Thermal conversion to PdO provides active redox surfaces capable of controlled oxidative catalysis.
Pharmaceutical Intermediate Synthesis
Enables key reduction and deprotection steps in API manufacturing, offering scalability, easy filtration, and high functional group tolerance. Its defined conversion profile supports reproducibility in regulated production environments.
Palladium Nanoparticle Synthesis
Facilitates controlled reduction to generate Pd nanoparticles or colloids for electrocatalysis, sensors, and advanced materials research with uniform size distribution. Reduction parameters such as temperature and reducing agent concentration influence particle morphology and catalytic performance.
Catalyst Recycling & Regeneration
Employed in processes requiring Pd recovery and reprecipitation, supporting cost-effective and sustainable catalyst management in industrial operations. The hydroxide form enables efficient reprocessing into active catalytic species.
For a broader overview of palladium material categories—including salts, oxides, supported catalysts, and organometallic systems across industrial applications—refer to
Palladium Compounds: Applications, Categories & Industrial Uses.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for Your Palladium(II) Hydroxide Supply?
Partner with Aure Chemical for Palladium(II) Hydroxide to benefit from premium reactivity, customization flexibility, and secure precious metal supply for your catalytic needs.
Consistent Palladium Content & Activity
Precise analytical control ensures uniform Pd content, controlled hydration, and reproducible performance in catalyst preparation and reduction.
Custom Precursor Formulations
Tailored Pd percentage, moisture levels, particle morphology, and supported variants to perfectly match your impregnation or synthesis process.
Secure Palladium Supply Chain
Responsible sourcing, strategic inventory management, and transparent pricing to mitigate volatility and ensure uninterrupted availability.
Technical Application Support
Dedicated specialists provide guidance on reduction protocols, support impregnation, activation, and catalyst optimization for maximum efficiency.
Regulatory & Sustainability Compliance
Full COA, REACH, RoHS, SDS documentation and palladium recycling programs aligned with global standards and ESG commitments.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Skin Irritation (Category 2); Eye Irritation (Category 2A); Specific Target Organ Toxicity, Single Exposure (respiratory) (Category 3); Aquatic Chronic (Category 3)
Hazard Statements: H315: Causes skin irritation; H319: Causes serious eye irritation; H335: May cause respiratory irritation; H413: May cause long lasting harmful effects to aquatic life
UN Number: Not regulated
Hazard Class: Not classified as hazardous for transport
Packing Group: Not applicable
 GHS07: Exclamation mark (irritant, respiratory)
GHS07: Exclamation mark (irritant, respiratory) GHS09: Environment (aquatic hazard)
GHS09: Environment (aquatic hazard)
