Aure Chemical: Your Reliable Partner for Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate (BF₃·2H₂O)
Aure Chemical is a trusted provider of high-quality Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate (BF₃·2H₂O), a versatile and potent chemical compound. This material serves as both a strong Bronsted acid and a Lewis acid, offering unique reactivity that makes it an invaluable catalyst and intermediate in various chemical processes.
Basic Information of Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate
Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate (CAS No. 13319-75-0) is characterized by its essential properties, ensuring its effectiveness in demanding applications:
| CAS No.: | 13319-75-0 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 231-569-5 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | BF₃·2H₂O |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 103.84 |
|---|
| Appearance: | Transparent Liquid |
|---|
| Melting point: | 6 ℃ |
|---|
| Boiling point: | 58 ℃ - 60 ℃ |
|---|
| Density: | 1.636 g/cm³ |
|---|
| Solubility | Low solubility in water; highly soluble in most organic solvents. |
|---|
| Nature: | Strong inorganic acid, highly corrosive, strong Lewis acid properties (derived from BF₃). |
|---|
| RIDADR: | UN 1743 8/PG 2 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 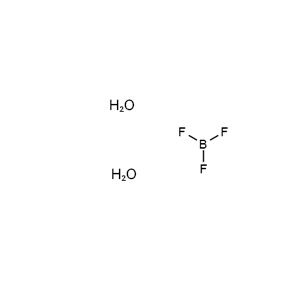 |
|---|
Its consistent quality and well-defined acidic properties make it a preferred choice for reactions requiring robust protonation or Lewis acid catalysis in an aqueous environment.
Primary Functions and Applications of Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate
The dual acidic nature and strong catalytic capabilities of Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate lead to its critical applications across various industries:
Versatile Acid Catalyst in Organic Synthesis:
Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate acts as a highly effective acid catalyst in a broad spectrum of organic reactions. Its strong Bronsted acidity (from protonated water) combined with the Lewis acidity of the BF₃ component allows it to effectively promote various transformations, including:
It's particularly useful in reactions where a strong, non-oxidizing acid catalyst is required, and the presence of water is tolerated or beneficial.
Polymerization reactions (e.g., initiation of cationic polymerization of olefins, epoxides)
Esterification and Etherification
Alkylation reactions
Condensation reactions
Key Intermediate for Specialty Chemicals:
This complex serves as a vital intermediate in the synthesis of a wide range of specialty chemicals. It can be used as a source of boron, fluorine, or both, in the preparation of other specific boron-containing compounds or as a reagent in various chemical processes that benefit from its unique reactivity profile.
Precursor for Aqueous Boron Fluoride Solutions:
Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate can be utilized as a convenient precursor for preparing various aqueous solutions containing boron fluoride species, which can then be tailored for specific industrial applications, such as certain surface treatments or electroplating solutions where precise control of fluoride and boron ions is necessary.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for Your Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate Needs?
Aure Chemical is dedicated to supplying high-quality chemical solutions with unwavering reliability. By partnering with us for your Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate requirements, you gain access to:
Guaranteed Purity & Consistent Performance: Our BF₃·2H₂O undergoes stringent quality control to ensure high purity and reliable catalytic activity, crucial for sensitive synthetic processes.
Reliable Supply Chain: We maintain a robust and efficient global supply chain, ensuring the timely and secure delivery of this essential chemical to your facilities.
Expert Technical Support: Our team of experienced chemists and technical specialists is readily available to provide comprehensive guidance on product application, safe handling, and storage.
Commitence to Quality & Safety: We adhere to the highest industry standards for quality management, safety, and environmental responsibility throughout our operations, from manufacturing to distribution.
Choose Aure Chemical for a trustworthy and dependable supply of high-quality Boron Trifluoride Dihydrate. We are ready to support your most complex chemical challenges.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Corrosive (GHS05), Acute Toxicity (GHS06), Health Hazard (GHS08)
Hazard Statements: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage; toxic if swallowed or in contact with skin; may cause respiratory irritation; suspected of causing genetic defects.
UN Number: UN 1743
Hazard Class: 8 (Corrosive Substances)
Packing Group: II
 GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive GHS06: Acute Toxicity
GHS06: Acute Toxicity GHS08: Health Hazard
GHS08: Health Hazard
