Explore Top-Quality Tripropylamine with Aure Chemical
Tripropylamine (TPA) is a tertiary aliphatic amine commonly used as a catalyst, organic synthesis intermediate, and multifunctional solvent. With strong hydrophobicity and excellent stability, it is widely incorporated in chemical manufacturing processes requiring controlled reactivity and compatibility with non-polar systems.
Basic Information of Tripropylamine
Tripropylamine (CAS No. 102-69-2) is meticulously produced and rigorously tested to meet stringent quality standards. We ensure exceptional purity and consistent performance, essential for your critical applications:
| CAS No.: | 102-69-2 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 203-047-7 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | C9H21N |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 143.27 |
|---|
| Appearance: | Colorless to pale yellow liquid |
|---|
| Odor: | Amine-like, mild |
|---|
| Melting Point: | −93.5 °C(lit.) |
|---|
| Boiling Point: | ~156–158°C |
|---|
| Density: | ~0.75 g/cm³ |
|---|
| Solubility: | Miscible with organic solvents; limited solubility in water |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 98 °F |
|---|
| RIDADR: | UN 2260 3/PG 3 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 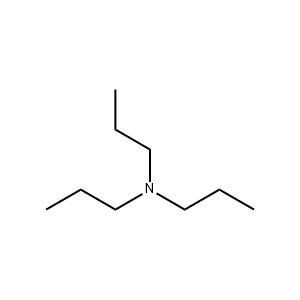 |
|---|
Application Overview
Tripropylamine is widely used in multiple industrial segments due to its catalytic activity, hydrophobic behavior, compatibility with non-aqueous systems, and chemical stability. Its primary applications include:
Phase-Transfer Catalyst: Facilitates reactions between immiscible phases, especially in alkylation, esterification, and polymer modification.
Pharmaceutical Intermediate: Used in synthesizing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), specialty amines, and quaternary ammonium compounds.
Agrochemical Ingredient: Applied in formulating herbicides, insecticides, and pesticide intermediates requiring tertiary amine structures.
Industrial Solvent: Effective in coatings, resins, and organic reaction systems where non-polar solvent properties are needed.
Chemical Synthesis: Serves as a precursor in manufacturing surfactants, corrosion inhibitors, flotation agents, and fine chemical additives.
Polymer and Material Processing: Utilized in producing specialty polymers, curing agents, and crosslinking systems.
Quaternization Reactions: Acts as a building block in synthesizing quaternary ammonium salts for surfactants and specialty chemicals.
Why Choose Aure Chemical
Engineering-Oriented Production: Our manufacturing process is optimized using advanced reaction control systems, ensuring consistent purity for demanding industrial applications.
Reliable Lead Times: We maintain strategic inventory levels and streamlined logistics networks to ensure stable and predictable global delivery.
Compliance and Documentation: Every batch is supported by COA, MSDS, TDS, and regulatory documentation suitable for international market requirements.
Flexible Customization: We provide adjustable purity levels, stabilized formulations, and tailored packaging options to align with unique production needs.
Technical Guidance: Our application specialists assist with formulation optimization, process selection, and compatibility evaluation.
Long-Term Supply Stability: Aure Chemical maintains multi-site production capability to minimize risk and guarantee uninterrupted supply.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Flammable Liquid (GHS02), Corrosive (GHS05), Acute Toxicity (GHS06), Health Hazard (GHS08)
Hazard Statements: Flammable liquid and vapor; causes severe skin burns and eye damage; harmful if swallowed, in contact with skin, or if inhaled; may cause respiratory irritation.
UN Number: UN 2260
Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable Liquids)
Packing Group: III
 GHS02: Flammable
GHS02: Flammable GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive GHS06: Acute toxicity
GHS06: Acute toxicity GHS08: Health hazard
GHS08: Health hazard
