Explore Top-Quality Diisopropylamine with Aure Chemical
Diisopropylamine (DIPA) is a secondary aliphatic amine known for its moderate basicity, low nucleophilicity, and excellent compatibility with organic synthesis processes. It serves as a valuable building block and catalyst component across pharmaceutical, agrochemical, and fine-chemical manufacturing.
Basic Information of Diisopropylamine
Diisopropylamine (CAS No. 108-18-9) is meticulously produced and rigorously tested to meet stringent quality standards. We ensure exceptional purity and consistent performance, essential for your critical applications:
| CAS No.: | 108-18-9 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 203-558-5 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | C6H15N |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 101.19 |
|---|
| Appearance: | Colorless to pale yellow transparent liquid |
|---|
| Odor: | Amine. |
|---|
| Melting Point: | -61 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Boiling Point: | ~83–85°C |
|---|
| Density: | ~0.72 g/cm³ |
|---|
| Solubility: | Miscible with organic solvents; limited solubility in water |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 1.4 °F |
|---|
| RIDADR: | UN 1158 3/PG 2 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 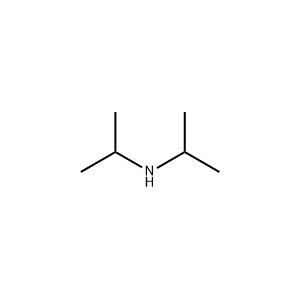 |
|---|
Application Overview
Diisopropylamine is widely applied in industrial and laboratory synthesis due to its steric hindrance, reduced reactivity compared to primary amines, and suitability for non-nucleophilic base applications. Its major uses include:
Pharmaceutical Synthesis: Key intermediate for APIs, peptide coupling reagents, and protective-group chemistry.
Non-Nucleophilic Base Reactions: Often converted to lithium diisopropylamide (LDA), a standard strong base in organometallic chemistry.
Agrochemical Manufacturing: Precursor for pesticide intermediates, herbicide building blocks, and selective crop-protection agents.
Catalyst and Processing Aid: Utilized in catalytic systems requiring controlled basicity and limited nucleophilicity.
Fine Chemical Intermediates: Supports synthesis of specialty solvents, stabilizers, and advanced organic materials.
Polymer and Resin Processing: Applied in producing curing agents, performance modifiers, and functional polymer intermediates.
Electronic Chemicals: Suitable for precision synthesis steps within semiconductor and microelectronics materials.
Why Choose Aure Chemical
Process-Driven Quality Assurance: Our automated purification and distillation systems ensure narrow impurity profiles, ideal for high-specification chemical processes.
Regulatory-Ready Supply: We support global compliance requirements with detailed documentation including COA, MSDS, TDS, and impurity maps.
Application-Centric Expertise: Aure Chemical’s technical team assists customers in pairing DIPA with appropriate reaction systems, solvents, and catalytic conditions.
Stability in Long-Term Contracts: Multi-region production capabilities and secure raw-material partnerships ensure reliable long-term delivery.
Custom Solution Options: Tailored purity grades, low-water specifications, and specialized packaging formats are available upon request.
Global Support Network: Regional distribution centers and responsive logistics teams provide efficient fulfillment and responsive after-sales service.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Flammable Liquid (GHS02), Corrosive (GHS05), Acute Toxicity (GHS06), Health Hazard (GHS08)
Hazard Statements: Highly flammable liquid and vapor; causes severe skin burns and eye damage; harmful if swallowed, in contact with skin, or if inhaled; may cause respiratory irritation.
UN Number: UN 1158
Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable Liquids)
Packing Group: II
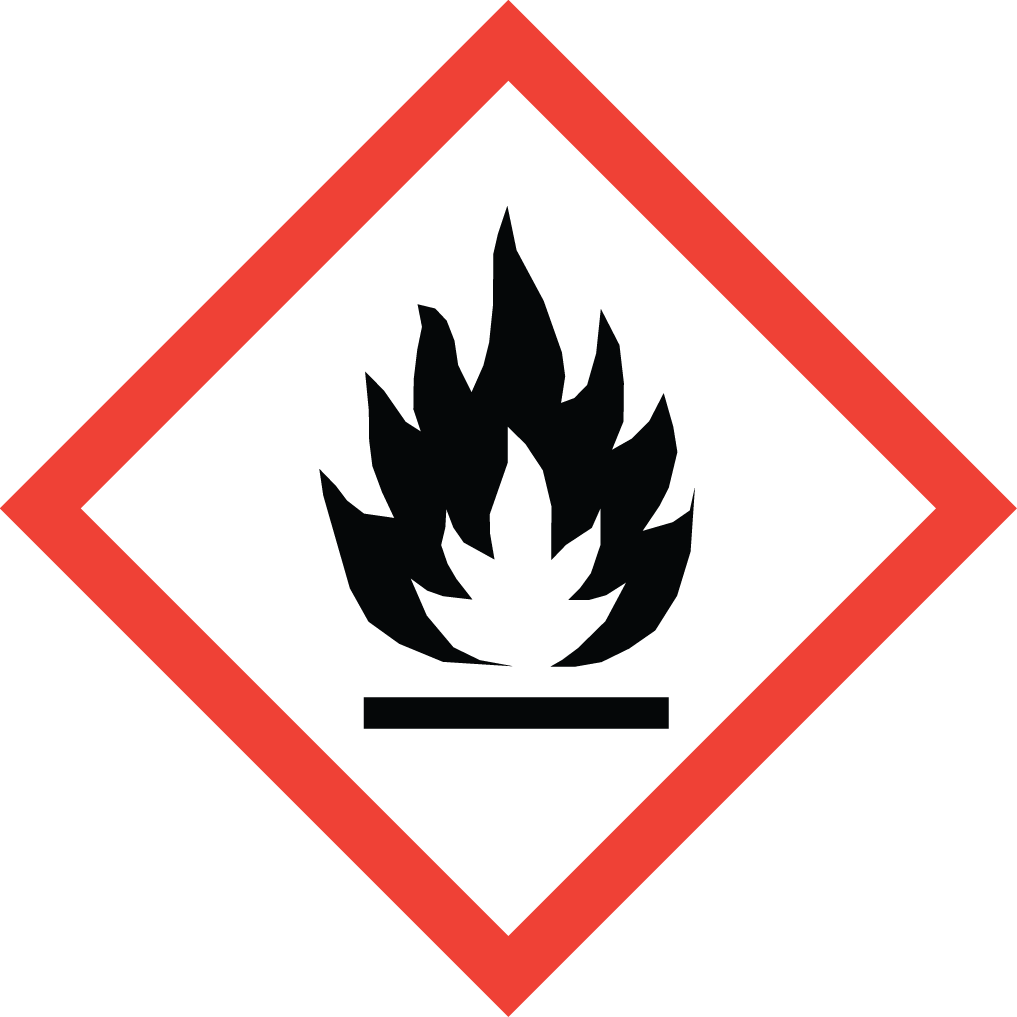 GHS02: Flammable
GHS02: Flammable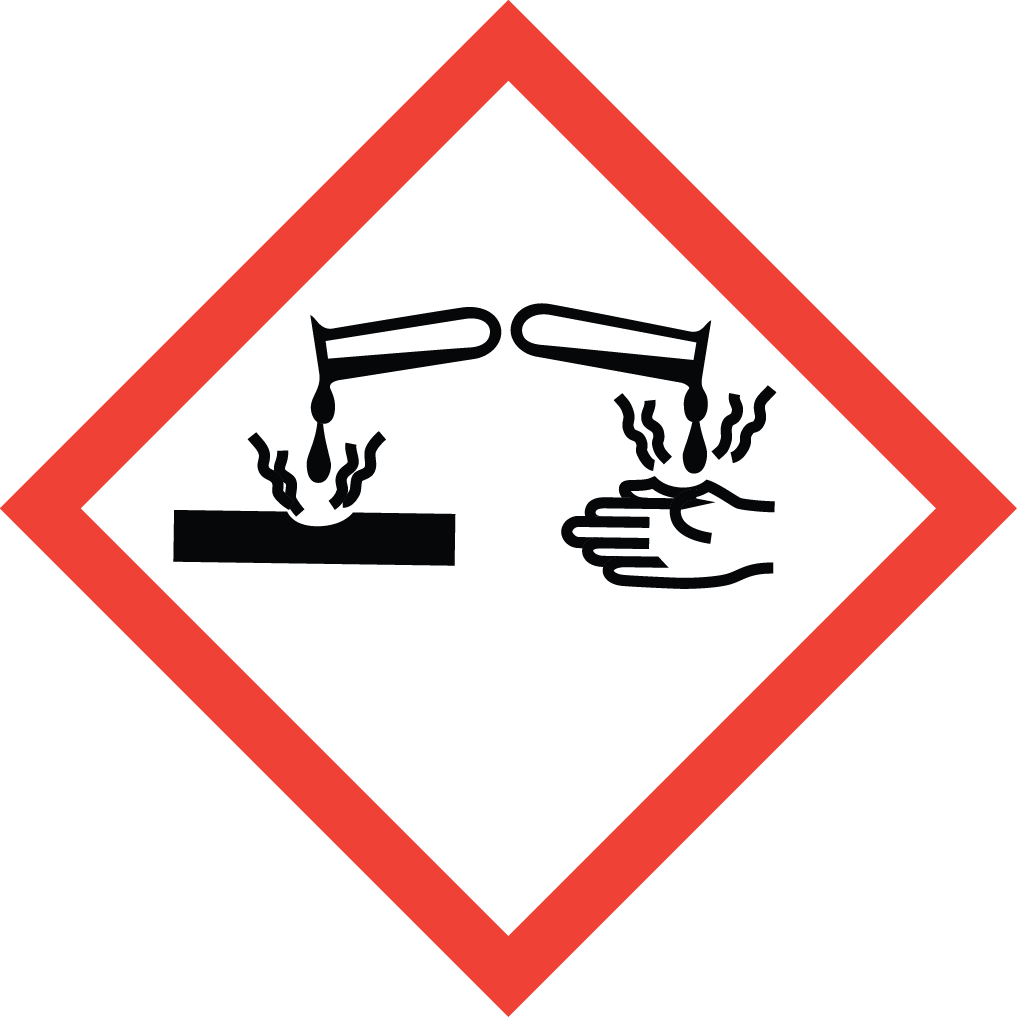 GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive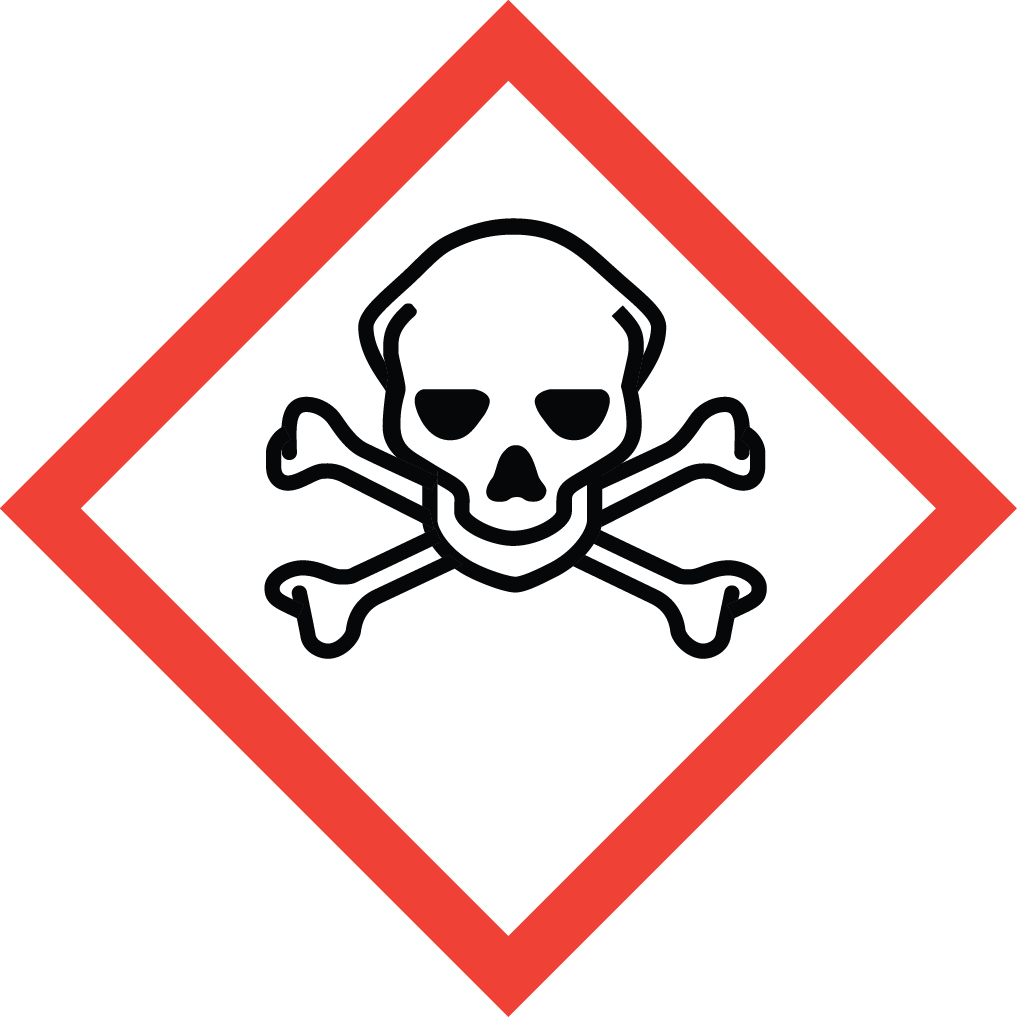 GHS06: Acute toxicity
GHS06: Acute toxicity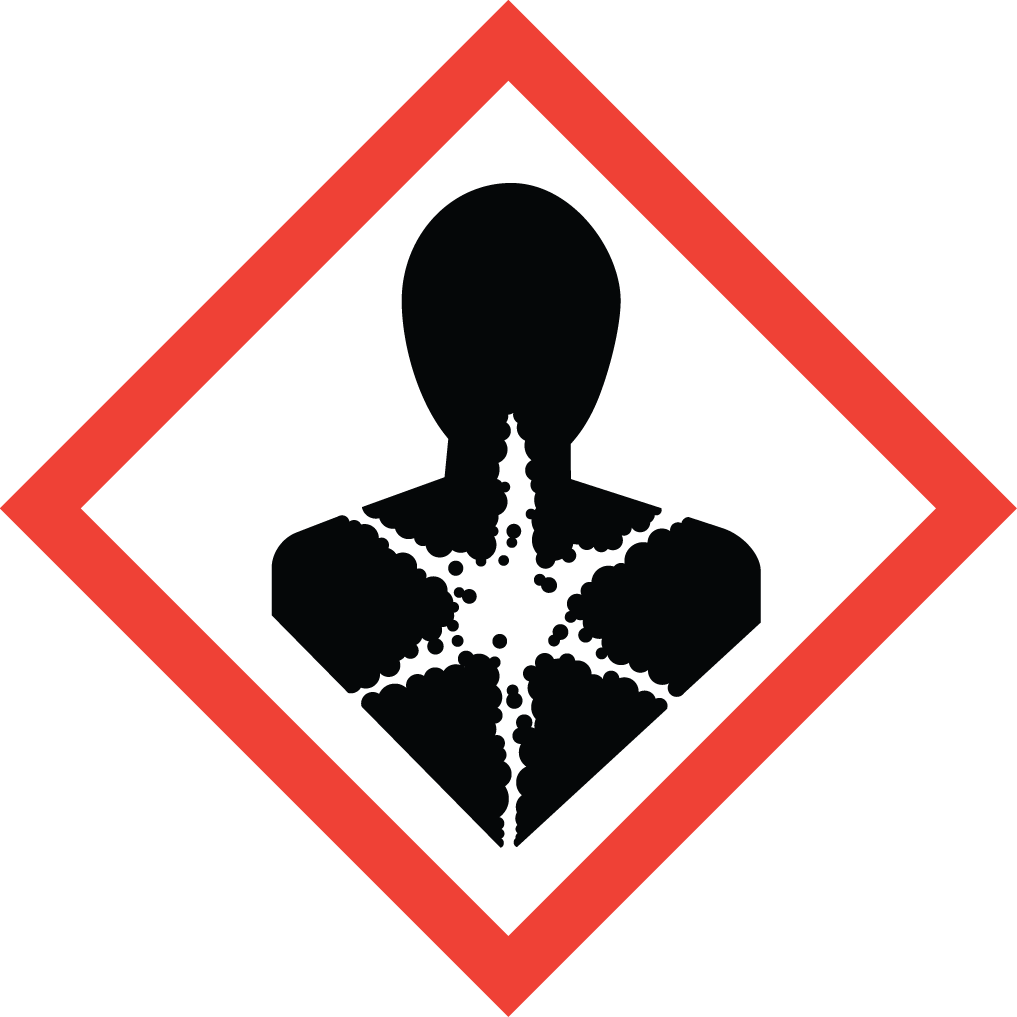 GHS08: Health hazard
GHS08: Health hazard
