Aure Chemical Delivers Excellence in BTDA
3,3′,4,4′-Benzophenone Tetracarboxylic Dianhydride (BTDA, CAS 2421-28-5) is an aromatic dianhydride primarily used as a monomer for synthesizing polyimides and as a curing agent for epoxy resins, offering high thermal stability, mechanical strength, flexibility, solubility, and processability due to its keto and carbonyl groups.
Basic Information of BTDA
| Product Name | 3,3',4,4'-Benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride |
|---|
| Abbreviation | BTDA |
|---|
| CAS Number | 2421-28-5 |
|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H6O7 |
|---|
| Molecular Weight | 322.23 g/mol |
|---|
| Appearance | Off-white to brown needles or crystalline powder |
|---|
| Purity | ≥98% |
|---|
| Package | 1kg/bottle, 20kg/drum, or customized |
|---|
| Molecular formula | 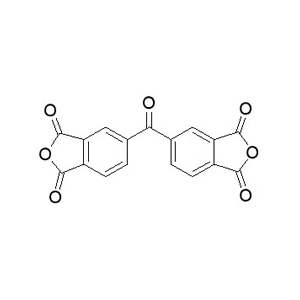 |
|---|
Key Properties
High thermal stability and rigidity derived from aromatic benzophenone dianhydride backbone
Keto (carbonyl) groups increase intermolecular spacing, improving solubility and processability of polyimide precursors
Excellent mechanical strength and dimensional stability in cured polyimide systems
Broad compatibility with various aromatic and aliphatic diamines for tailored electronic-grade polyimides
Balanced dielectric and structural performance suitable for electronic and high-temperature insulation materials
Key Applications of BTDA
Electronics and Microelectronics (Primary Application):
Widely used in electronic-grade polyimide films for electrical insulation, flexible copper-clad laminates (FCCL),
wire enamels and varnishes for motors, dielectric layers in memory devices and organic electronics.BTDA-based polyimides are widely applied in electronic and microelectronic systemsdue to their balanced thermal, mechanical, and dielectric performance.
Functional and Research-Oriented Polyimide Systems:
Explored in energy-related and photocatalytic applications, including photosensitizers and functional membranes,
where BTDA-based polyimides serve as stable structural platforms for advanced material research.

