Discover Aure Chemical's Premium α-Pinene Oxide Supply
α-Pinene Oxide, CAS 1686-14-2, is a bicyclic epoxide derived from the natural terpene, $\alpha$-Pinene. It is a key intermediate in the specialty chemical industry, valued for its unique, strained three-membered epoxy ring structure. This structure makes it highly reactive, enabling its conversion into a wide range of valuable downstream chemicals, particularly in the fragrance and flavor sectors. It is typically a colorless to pale yellow, clear liquid.
Basic Information of α-Pinene Oxide
Meticulously produced and rigorously tested to meet stringent quality standards. We ensure exceptional purity and consistent performance, essential for your critical applications:
| CAS No.: | 1686-14-2 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 216-869-6 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | C10H16O |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 152.23 |
|---|
| Appearance: | Colorless to pale yellow clear liquid |
|---|
| Odor: | Characteristic fresh, piney, camphor-like odor |
|---|
| Boiling Point: | 185 °C |
|---|
| Density:0.964 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) | 0.964 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Solubility: | Immiscible with water; highly soluble in organic solvents (alcohol, ether, terpenes). |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 150 °F |
|---|
| RIDADR: | 3082 9/PG 3 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 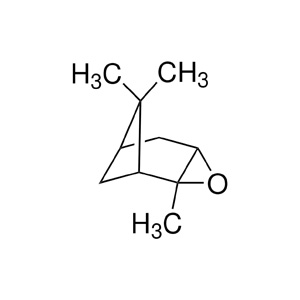 |
|---|
Application Overview
α-Pinene Oxide is a highly versatile chemical intermediate, primarily utilized for the selective synthesis of complex natural product derivatives:
Fragrance and Aroma Chemicals: It is a key precursor for the synthesis of high-value fragrance molecules. Ring-opening and rearrangement reactions lead to compounds like campholenic aldehyde, which is, in turn, an essential starting material for several synthetic musk fragrances (e.g., Cyclacene) and sandalwood notes.
Flavoring Agents: Derivatives of $\alpha$-Pinene Oxide are used to create specific minty, camphoraceous, or pine-like flavor notes for food and beverage applications, requiring high purity to meet regulatory standards.
Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Its strained epoxide ring is easily opened by nucleophiles, enabling the stereoselective synthesis of complex chiral alcohols and amino-alcohols. These are critical intermediates in the development of certain drug candidates and pharmaceutical precursors.
Polymer and Resins: It can be used as a co-monomer or reactive diluent in specialty polymer systems. The ring-opening polymerization of epoxides yields polyols, which are components of specialized polyurethane or epoxy resins, improving flexibility and adhesion.
Fine Chemical Synthesis: The molecule is employed in asymmetric synthesis as a chiral auxiliary or starting material, where its inherent stereochemistry is transferred to the final product.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for α-Pinene Oxide?
Aure Chemical ensures that your supply of α-Pinene Oxide (CAS 1686-14-2) meets the highest standards required for demanding flavor and fragrance applications.
Isomeric Purity Certification: α-Pinene Oxide exists as two enantiomers (cis- and trans-). We offer product with certified cis/trans ratios and high enantiomeric excess (ee) purity. This control is vital, as the ratio significantly dictates the odor profile and reactivity, preventing off-notes in your final fragrance or flavor product.
Natural Origin Traceability: Our α-Pinene Oxide is synthesized from sustainably sourced natural $\alpha$-Pinene feedstock, providing full traceability from the natural source to the final product. This meets the growing consumer and regulatory demand for transparency in natural chemical supply chains.
Specialized Stabilization Protocol: Terpene oxides can be sensitive to heat and light. We utilize custom-designed packaging and dark storage environments to prevent thermal and light-induced degradation, guaranteeing that the high-quality odor and reactivity profile are preserved throughout shipping and storage.
Expert Regulatory Support: We provide comprehensive regulatory documentation tailored for the fragrance and flavor industries (e.g., IFRA and FEMA compliance checks), simplifying your submission processes for new product development involving this key ingredient.
Hazards Classification
 GHS06: Acute toxicity
GHS06: Acute toxicity
