Premium Diallylamine Solutions by Aure Chemical
Diallylamine (CAS 124-02-7) is a reactive secondary amine featuring two allyl groups, offering strong utility
as an intermediate in polymer synthesis, specialty monomers, pharmaceutical development, and agrochemical
manufacturing. Its dual allylic structure provides selective reactivity for alkylation, Mannich reactions,
functional polymerization, and fine-chemical synthesis. Aure Chemical supplies high-purity industrial and
specialty grades supported with consistent quality, technical documentation, and flexible packaging options
for laboratory, pilot, and commercial-scale applications.
Basic Information of Diallylamine
Meticulously produced and rigorously tested to meet stringent quality standards. We ensure exceptional purity and consistent performance, essential for your critical applications:
| CAS No.: | 124-02-7 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 204-671-2 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | C6H11N |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 97.16 g/mol |
|---|
| Appearance: | Colorless to pale yellow liquid |
|---|
| Odor: | Characteristic amine odor |
|---|
| Melting Point: | -88 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Boiling Point: | 111-112 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Density: | Approx. 0.78–0.81 g/cm³ (batch dependent) |
|---|
| Solubility: | Soluble in many organic solvents; limited solubility in water |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 60 °F |
|---|
| RIDADR: | UN 2359 3/PG 2 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 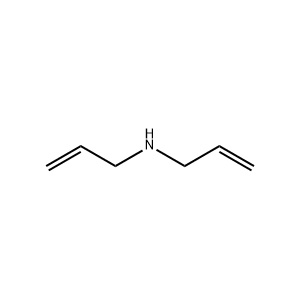 |
|---|
Application Overview
Diallylamine is a versatile building block widely used across multiple industrial sectors. Its electron-rich
allyl groups and secondary amine functionality enable diverse transformations, making it valuable in:
Polymer & Monomer Synthesis: Used to produce diallyl monomers, crosslinking agents, reactive polymer modifiers, and specialty resins with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties.
Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Suitable for multi-step synthesis where allylic reactivity and amination pathways are required. Common in research routes for APIs and experimental compounds.
Agrochemical Manufacturing: Serves as a precursor for herbicide, pesticide, and plant-protection intermediates via controlled allylic substitution and addition reactions.
Surfactants & Functional Additives: Helps create specialty surfactants, corrosion inhibitors, and wetting agents where amine functionality is essential.
Fine Chemical Synthesis: Participates in Mannich reactions, alkylation steps, and cyclization pathways, enabling production of dyes, chelating agents, performance additives, and catalytic intermediates.
R&D and Pilot Projects: Commonly used in exploratory chemistry, polymer design studies, and reaction mechanism research due to its clean, predictable reactivity profile.
Why Choose Aure Chemical
Aure Chemical offers a reliable sourcing experience strengthened by process knowledge and customer-oriented service:
Stable Multi-Region Supply Chain: Diverse sourcing pathways ensure reliable material availability and reduced risk of supply interruptions.
Batch Consistency & Transparency: Every batch is supported by COA, detailed impurity data, and traceability to help customers maintain consistent process performance.
Technical Advisory Support: Application engineers can discuss reaction considerations, compatibility, and solvent selection tailored to diallylamine’s behavior.
Flexible Packaging Formats: Options include small-pack samples, laboratory bottles, industrial drums, and customized packaging to meet project scale.
Global Documentation Support: Assistance with SDS, transport classification, export paperwork, and regulatory compliance for international shipments.
Customer-Focused Lead Times: Efficient logistics and coordinated inventory planning ensure dependable delivery schedules for both recurring and project-based demand.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Flammable Liquid (GHS02), Acute Toxicity (GHS06), Corrosive (GHS05), Environmental Hazard (GHS09)
Hazard Statements: Highly flammable liquid and vapor; harmful if swallowed or if inhaled; toxic in contact with skin; causes severe skin burns and eye damage; harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
UN Number: UN 2359
Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable Liquids)
Packing Group: II
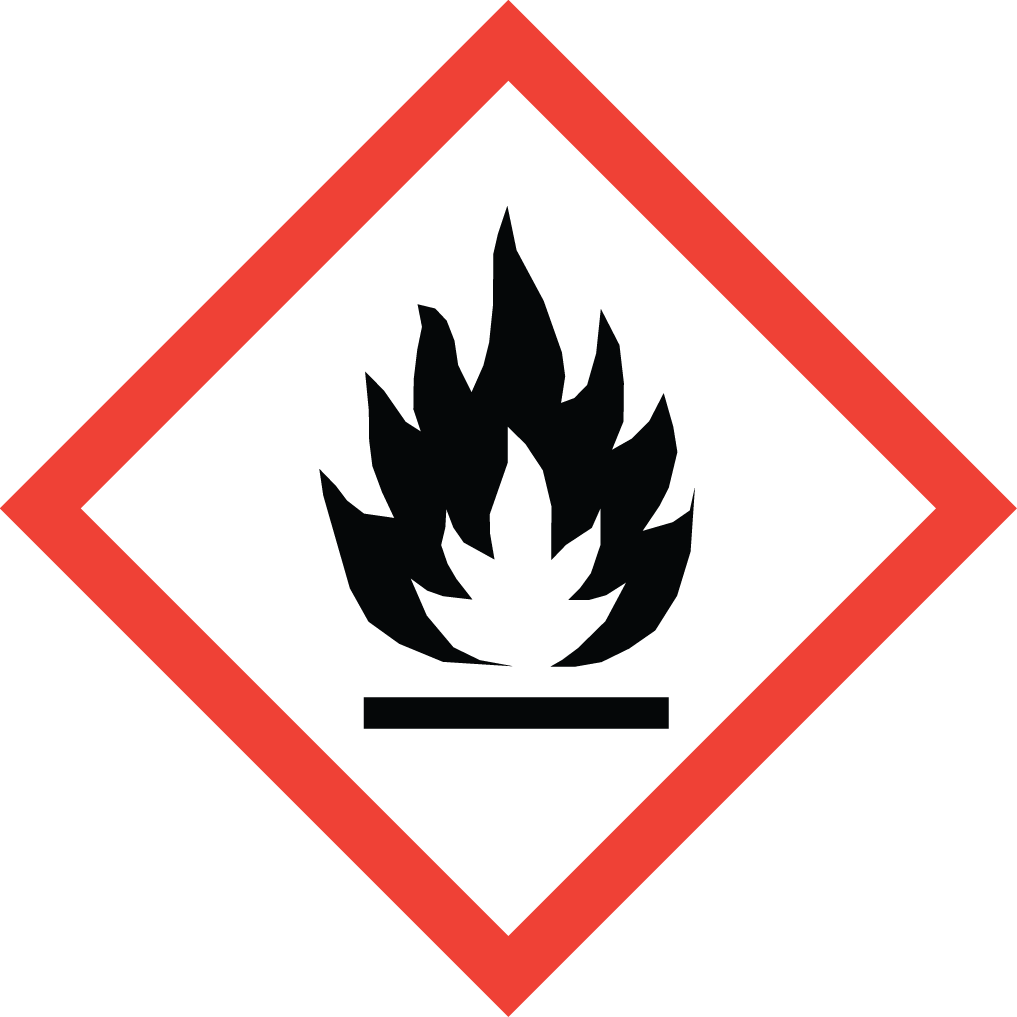 GHS02: Flammable
GHS02: Flammable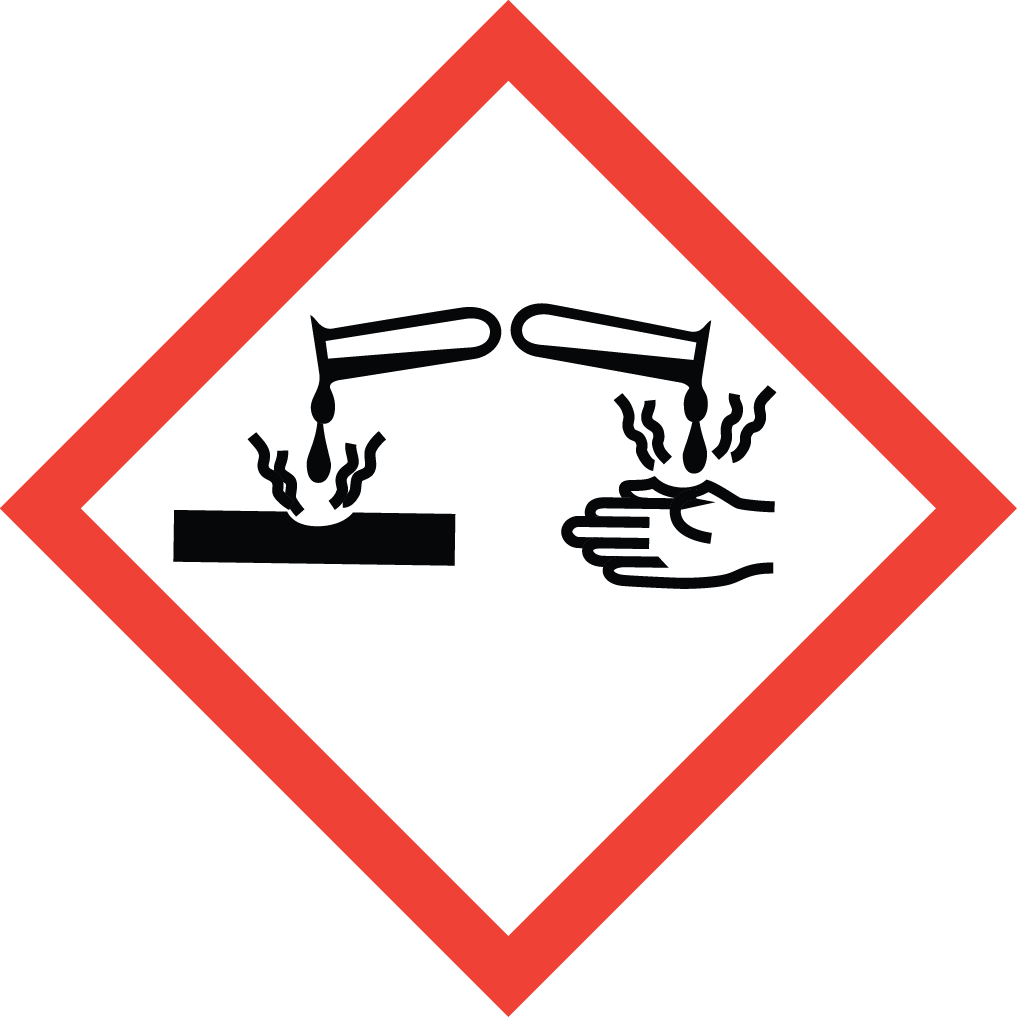 GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive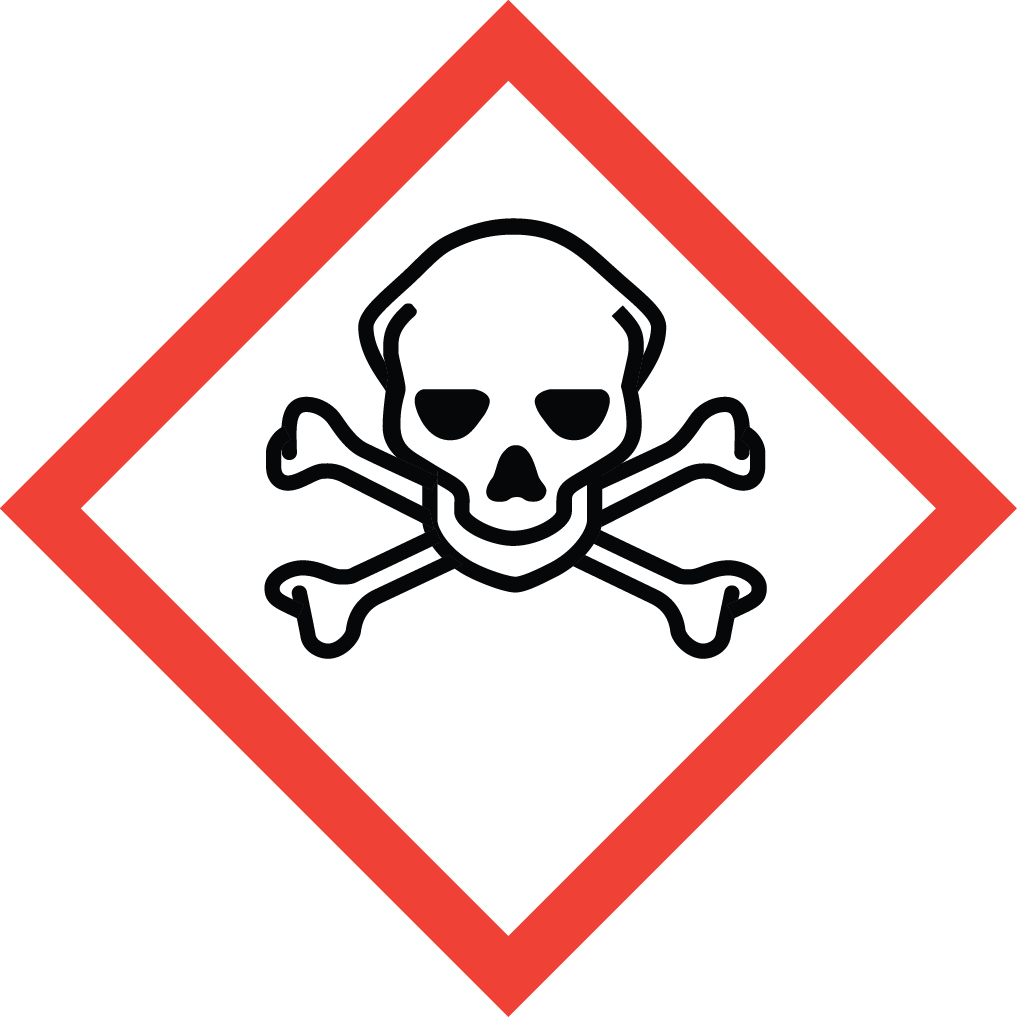 GHS06: Acute toxicity
GHS06: Acute toxicity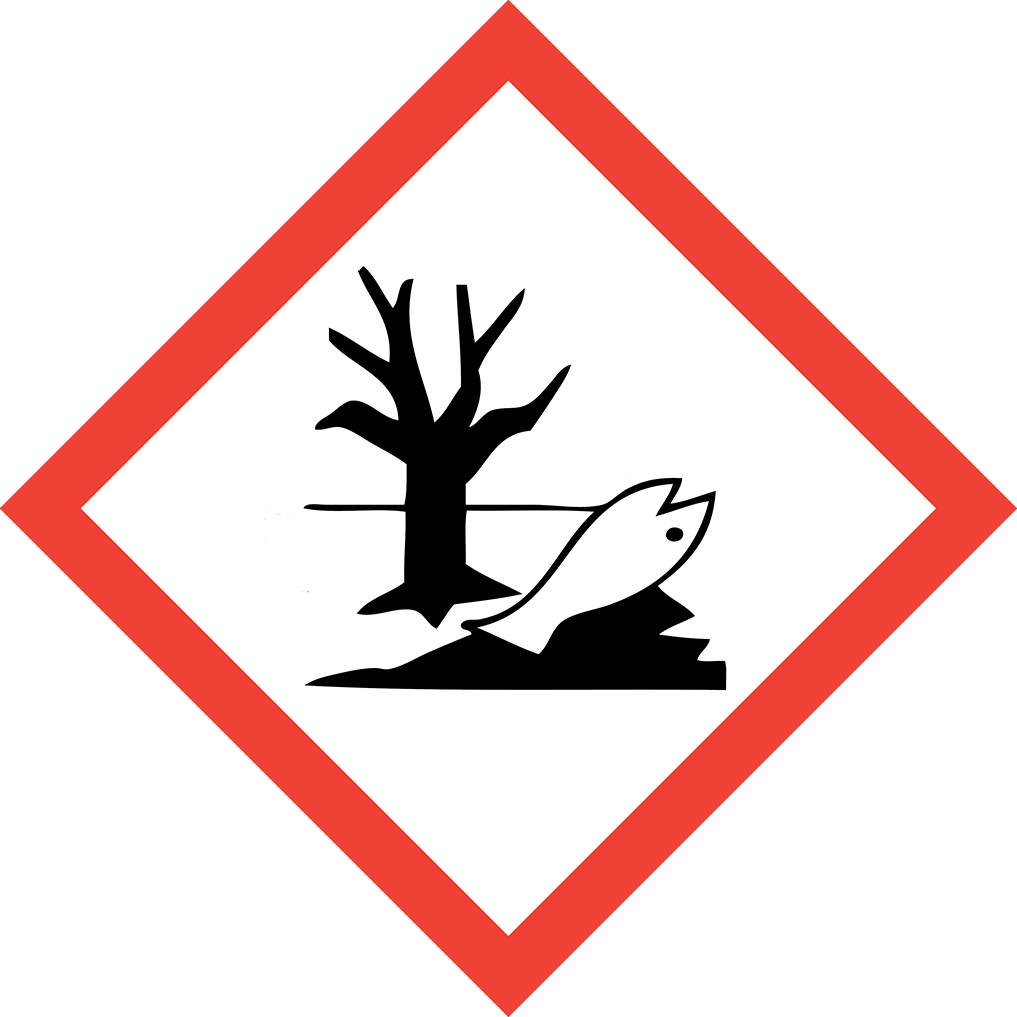 GHS09: Environmental hazard
GHS09: Environmental hazard
