Discover Aure Chemical's Premium Diisobutylamine Supply
Diisobutylamine is a tertiary aliphatic amine recognized for its low basicity, excellent solvency, and stable performance across a wide range of chemical processes. Its branched structure provides steric shielding useful in selective reactions, while its compatibility with organic solvents makes it valuable in extraction, catalysis, and synthesis workflows.
Basic Information of Diisobutylamine
Aure Chemical offers Diisobutylamine in high-purity grades suitable for pharmaceutical synthesis, agrochemical development, polymer modification, and specialty formulation applications. It is produced under strict quality standards to ensure consistent behavior in industrial and R&D settings.
| CAS No.: | 110-96-3 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 203-819-3 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | C8H19N |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 129.24 |
|---|
| Appearance: | Clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid |
|---|
| Odor: | Mild amine-like odor |
|---|
| Melting Point: | -77 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Boiling Point: | 137-139 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Density: | 0.74 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
|---|
| Solubility: | Highly soluble in organic solvents; low water solubility |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 85 °F |
|---|
| RIDADR: | UN 2361 3/PG 3 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 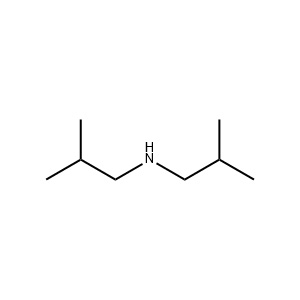 |
|---|
Application Overview
Diisobutylamine is valued across multiple industries due to its stability, liquid handling ease, and reactivity profile suited for selective transformations. It serves as an important intermediate and functional component in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, catalyst systems, and fine chemical production.
Pharmaceutical Synthesis: Used to produce intermediates, protecting groups, side-chain modifiers, and catalyst ligands in API manufacturing.
Agrochemical Development: Incorporated into the synthesis of herbicides, pesticide precursors, and nitrogen-containing crop protection molecules.
Extraction & Separation Processes: Acts as an organic phase amine extractant in metal ion extraction and purification systems.
Catalysis & Reaction Facilitation: Applied as a base, catalyst component, or sterically hindered amine in specialized reaction environments.
Polymer & Resin Industries: Utilized for producing curing agents, adhesion promoters, and resin modification intermediates.
Fine Chemical Synthesis: Used in custom molecule development, fragrance intermediates, dye precursors, and specialty organic compounds.
R&D and Pilot-Scale Chemistry: Favored for producing tertiary amine structures in research laboratories and scale-up operations.
Its low viscosity, controlled basicity, and steric hindrance enhance its suitability for processes requiring selective reactivity, mild catalytic behavior, and efficient solvent-phase operation.
Why Choose Aure Chemical
Aure Chemical provides premium-grade Diisobutylamine supported by a service model tailored for manufacturers, distributors, and research institutions. Our focus is delivering dependable quality, transparent documentation, and responsive technical assistance across global markets.
Rigorous Batch Consistency: Uniform specification control ensures predictable reaction performance from batch to batch.
Industry-Specific Packaging Options: From lab-scale bottles to bulk tank drums, we offer packaging suited for diverse operational needs.
Full Compliance Support: REACH, GHS, export documents, and regulatory certificates can be provided as required by regional markets.
Dedicated Technical Expertise: Our specialists assist with integration into synthesis pathways, extraction systems, or formulation processes.
Reliable Global Delivery: With optimized logistics and international shipping capabilities, we maintain dependable worldwide supply.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Flammable Liquid (GHS02), Acute Toxicity (GHS06), Corrosive (GHS05)
Hazard Statements: Flammable liquid and vapor; harmful if swallowed; harmful in contact with skin; harmful if inhaled; causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
UN Number: UN 2361
Hazard Class: 3 (Flammable Liquids)
Packing Group: III
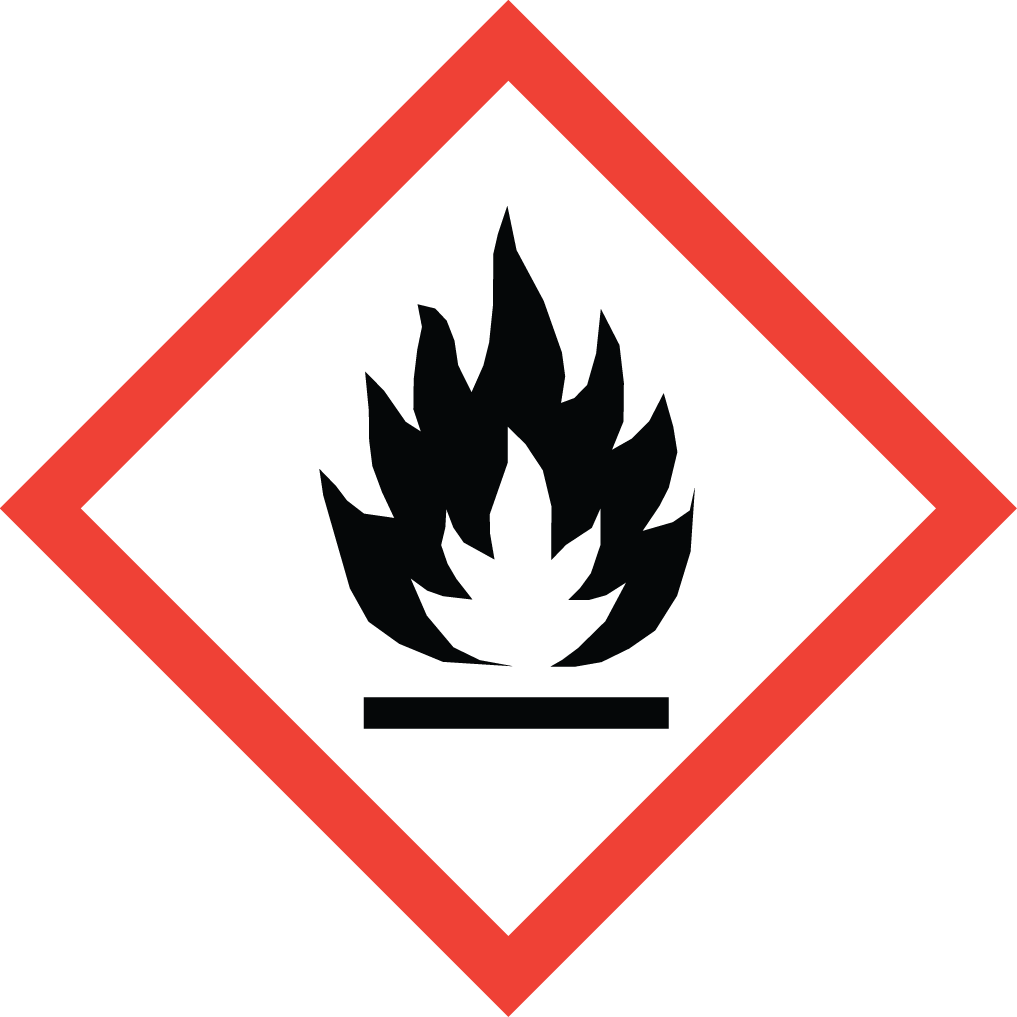 GHS02: Flammable
GHS02: Flammable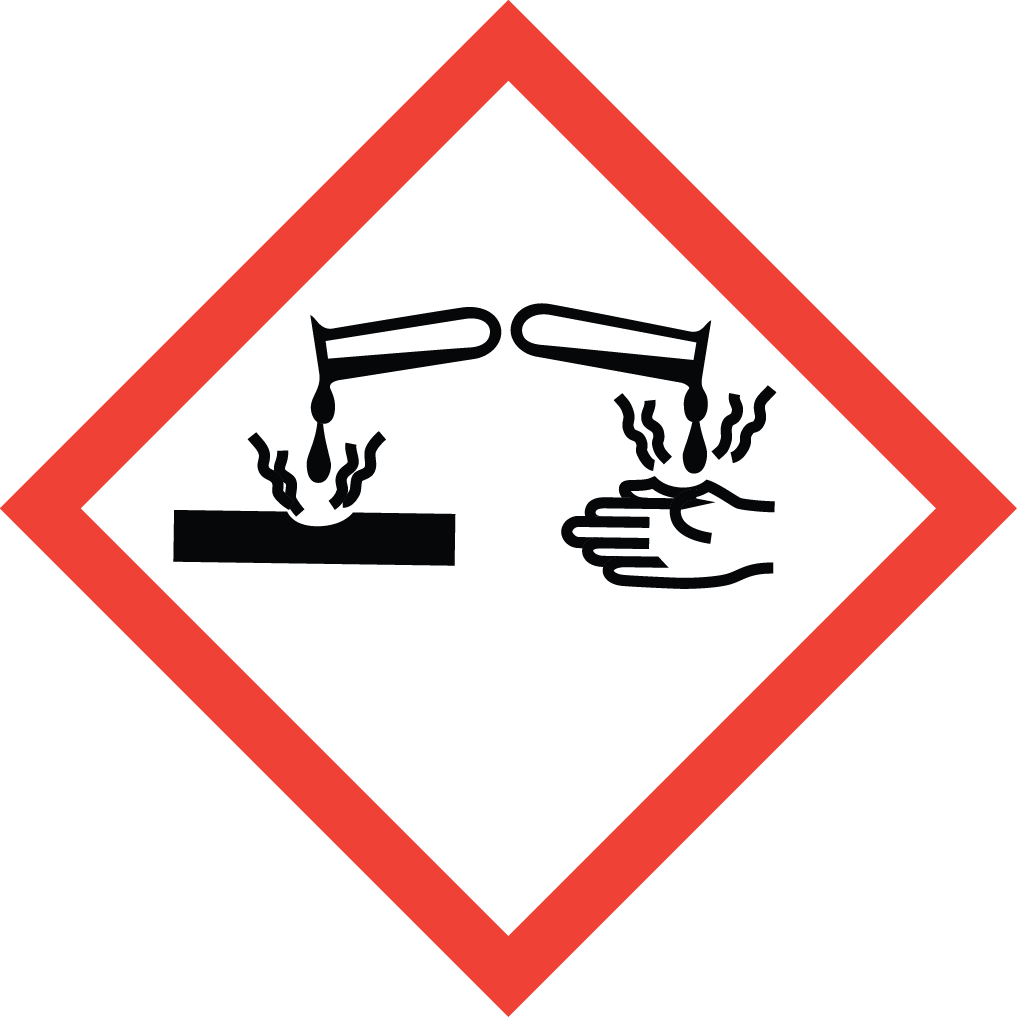 GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive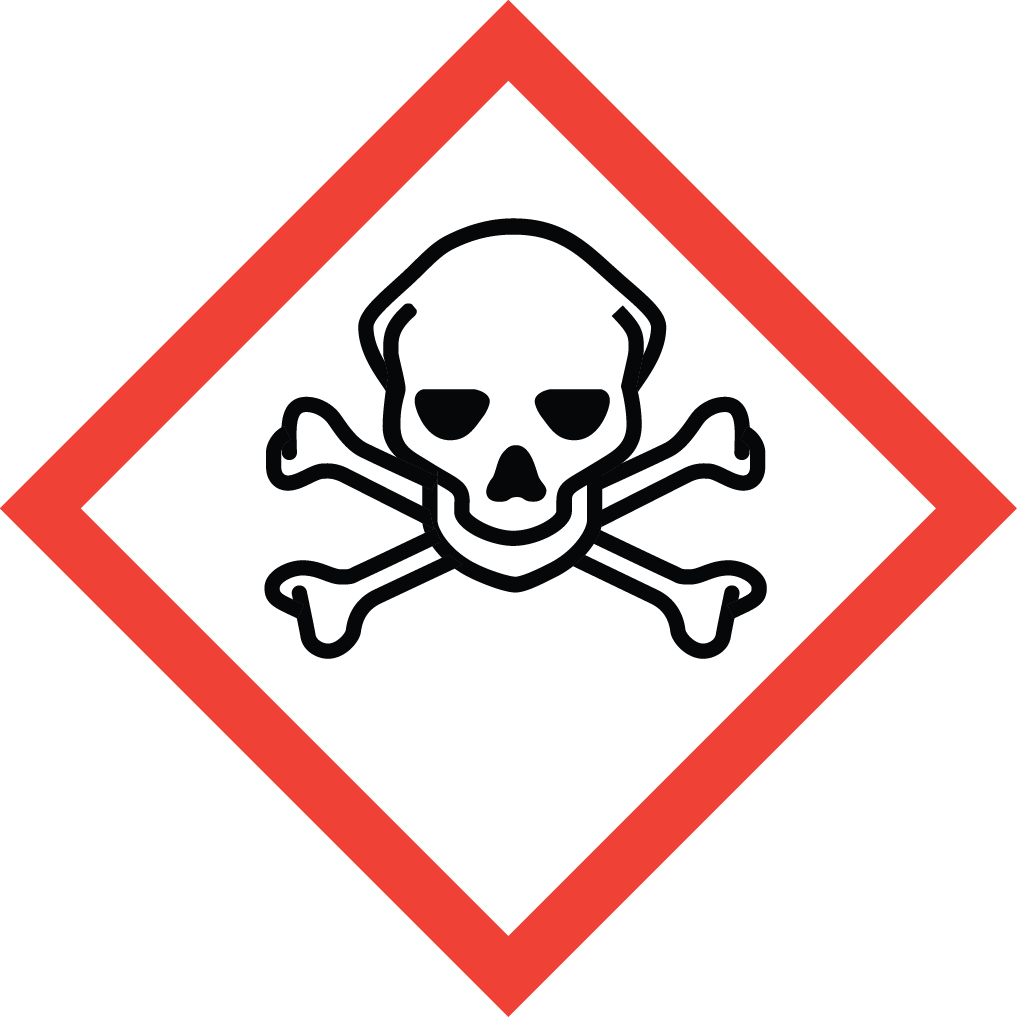 GHS06: Acute toxicity
GHS06: Acute toxicity
