Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO): Properties, Production, and Versatile Applications in Industry
Dimethyl sulfoxide, commonly abbreviated as DMSO, is a polar aprotic solvent widely recognized for its versatility in chemical, pharmaceutical, and industrial processes. This colorless liquid, with the chemical formula (CH₃)₂SO, originates from wood pulp processing and has become integral to many laboratory and manufacturing environments.
DMSO is valued for its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar compounds, enabling its use in synthesis, extraction, formulation, cleaning, and cryopreservation. Its high boiling point, thermal stability, and miscibility with water and many organic solvents support reliable performance across a wide range of applications.
This page provides an overview of DMSO’s physical and chemical properties, production routes, safety considerations, and main application areas.
Physical and Chemical Properties
DMSO exhibits a combination of properties that make it an effective solvent in demanding chemical environments. It boils at approximately 189°C and freezes at 18.5°C, providing a broad liquid temperature range. At 20°C, its density is about 1.10 g/cm³ and viscosity approximately 2.0 cP.
The solvent has a high dielectric constant (~47), which enables strong solvation of ionic and polar species. As an aprotic solvent, DMSO does not donate protons, allowing it to support reaction mechanisms that are inhibited in protic media. It is hygroscopic and readily absorbs moisture from air, which should be considered for moisture-sensitive processes.
DMSO is combustible with a flash point around 95°C and shows good stability under normal handling conditions.
Molecular Structure of DMSO
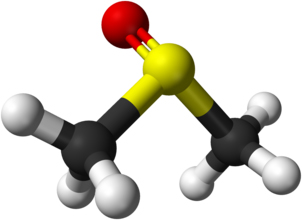
DMSO consists of a sulfur atom bonded to two methyl groups and double-bonded to an oxygen atom. This structure creates a strong dipole moment and an amphiphilic character, with both polar and non-polar regions present in the molecule.
The oxygen atom acts as a hydrogen-bond acceptor, while the methyl groups provide hydrophobic character. This dual nature explains DMSO’s ability to dissolve a wide range of chemical species.
Typical Physical Property Data
Molecular weight: 78.13 g/mol
Boiling point: 189°C
Melting point: 18.5°C
Density (20°C): ~1.10 g/cm³
Viscosity (20°C): ~2.0 cP
Autoignition temperature: ~215°C
Miscibility: Water, alcohols, ketones, many organic solvents
Production Methods of DMSO
Industrial DMSO is primarily produced by oxidation of dimethyl sulfide (DMS). DMS is commonly obtained as a by-product from kraft pulping operations in the paper industry.
Oxidation is carried out using air, oxygen, or nitrogen dioxide under controlled conditions. After reaction, purification is performed by distillation and additional polishing steps to achieve the desired purity grades.
Alternative synthetic routes involve production of DMS from methanol and hydrogen sulfide followed by oxidation.
Applications of Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
DMSO as Pharmaceutical Solvent
DMSO dissolves many active pharmaceutical ingredients with limited aqueous solubility and is commonly used during formulation development.
Learn more about how DMSO is used as a pharmaceutical solvent.
DMSO as Industrial Solvent
DMSO is used in industrial processing for polymer dissolution, resin handling, cleaning operations, and chemical manufacturing.
Learn more about how DMSO is applied as an industrial solvent.
DMSO for Electronics Cleaning
High-purity DMSO is used to remove photoresist, flux residues, and organic contaminants in semiconductor and PCB manufacturing.
Learn more about how DMSO is used for electronics cleaning.
DMSO as Reaction Solvent
DMSO serves as a polar aprotic reaction medium for oxidation, substitution, coupling, and other organic transformations.
Learn more about how DMSO is used as a reaction solvent.
DMSO as Extraction Solvent
DMSO is employed in liquid–liquid and solid–liquid extraction processes for separation and purification of chemical compounds.
Learn more about how DMSO is used as an extraction solvent.
DMSO as Cryoprotectant and Formulation Excipient
DMSO is widely used in cryopreservation of cells and microorganisms and as a formulation excipient in biotechnology and pharmaceutical research.
Learn more about how DMSO is used as a cryoprotectant and formulation excipient.
Dimethyl sulfoxide, commonly abbreviated as DMSO, is a polar aprotic solvent widely recognized for its versatility in chemical, pharmaceutical, and industrial processes. Dimethyl Sulfoxide (CAS 67-68-5)is available in high-purity grades from Aure Chemical.
Safety and Handling Considerations
DMSO readily penetrates skin and can carry dissolved substances into the body. Protective gloves and eye protection should be worn during handling.
Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area. Avoid contact with strong oxidizers. Refer to the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed guidance.
Regulatory and Compliance Overview
DMSO is registered under major chemical regulatory frameworks such as REACH in the EU and TSCA in the United States. Certain grades may comply with pharmacopeial standards (USP, EP) depending on specification.
Users should verify suitability of grade and compliance status for their intended application.
Market Overview and Industry Trends
Global demand for DMSO is driven by pharmaceutical manufacturing, electronics, biotechnology, and chemical processing. Interest in recyclable and high-purity solvents continues to support steady market growth.
Dimethyl Sulfoxide Market Size 2025 to 2035 (USD Million)
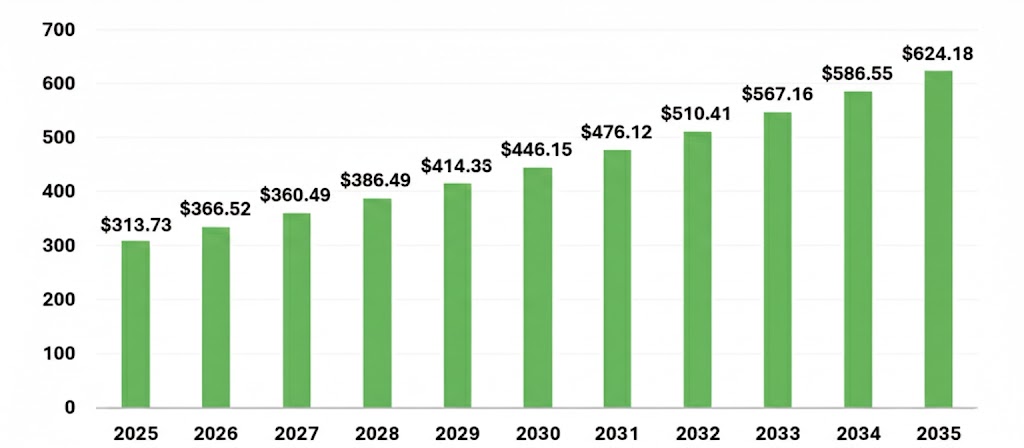
The global dimethyl sulfoxide market is projected to reach USD 313.73 million in 2025, with an expected increase from USD 336.32 million in 2026 to around USD 624.18 million by 2035. The market is forecasted to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.12% from 2026 to 2035.
Looking for a reliable bulk supplier of Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)?
Aure Chemical provides high-purity DMSO raw materials for the pharmaceutical, polymer, and chemical industries.
View our DMSO product page
