What is Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex
Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex (CAS 420-16-6), often abbreviated as BF₃·CH₃CN, is a stable Lewis acid adduct formed by 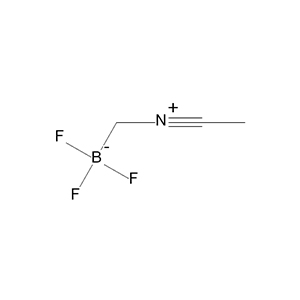 boron trifluoride coordinating with acetonitrile, making it a practical alternative to the more volatile BF₃ gas. This colorless to light yellow liquid is widely used in organic synthesis as a catalyst, where knowing its physical and chemical properties is crucial—like understanding the specs of a car engine before driving it—for safe handling, proper storage, and effective application in reactions. Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex (CAS 420-16-6) is a colorless liquid Lewis acid widely applied in organic synthesis. Its well-defined physical and chemical properties make it a preferred reagent for controlled catalytic reactions.
boron trifluoride coordinating with acetonitrile, making it a practical alternative to the more volatile BF₃ gas. This colorless to light yellow liquid is widely used in organic synthesis as a catalyst, where knowing its physical and chemical properties is crucial—like understanding the specs of a car engine before driving it—for safe handling, proper storage, and effective application in reactions. Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex (CAS 420-16-6) is a colorless liquid Lewis acid widely applied in organic synthesis. Its well-defined physical and chemical properties make it a preferred reagent for controlled catalytic reactions.
Basic Identification
For quick reference, here's a summary of the compound's key identifiers:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex |
| CAS Number | 420-16-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C₂H₃BF₃N |
| Molecular Weight | 108.86 g/mol |
| Synonyms | BF₃·CH₃CN, Boron Trifluoride–Acetonitrile Adduct |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid |
| Odor | Pungent or sweet like ether |
| Chemical Structure | (See below for visualization) |
Physical Properties
BF₃·CH₃CN exhibits properties that make it user-friendly in lab and industrial settings. Here's a detailed look:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Boiling Point | 85.5°C at 101.325 kPa (decomposes around 100–105°C) |
| Melting Point | Data not available (approx. −20°C) |
| Density | 0.87-0.88 g/mL at 20°C |
| Solubility | Miscible with organic solvents; easily soluble in water (reacts) |
| Vapor Pressure | 84.1-301 hPa at 20-50°C |
| Refractive Index | Not specified |
| Stability | Stable under dry, inert conditions |
These traits mean it's volatile enough to mix well but more stable than gaseous BF₃, like a bottled soda that's fizzy but won't explode if handled carefully. It reacts slowly with moisture, making dry conditions essential, and its liquid form simplifies dosing compared to gas cylinders.
Chemical Properties
Lewis Acid Character
As a strong Lewis acid, BF₃·CH₃CN accepts electron pairs from donors, facilitating reactions much like a vacuum cleaner sucking up dirt to clean a surface. The BF₃ moiety coordinates with electron-rich compounds such as ethers, nitriles, and amines, enabling catalysis in synthesis.
Reactivity
It reacts with moisture to form hydrofluoric acid (HF) and boric acid derivatives—imagine it fizzing like baking soda in vinegar but more hazardous. Incompatible with strong bases, oxidizing agents, and water, it decomposes upon exposure to water or alcohols, releasing toxic fumes. Stable in a dry, inert atmosphere, it's best kept under nitrogen or argon.
Complex Formation
The complex forms stable coordination with polar solvents, serving as a mild, controllable source of BF₃ for reactions, which enhances selectivity and control in organic transformations.
Spectral and Analytical Data
For analytical purposes, BF₃·CH₃CN shows characteristic peaks in IR spectra for B-F and C≡N stretching (around 1100-1200 cm⁻¹ for B-F and 2200 cm⁻¹ for CN, shifted due to coordination). In ¹⁹F NMR, it exhibits signals around -150 ppm, consistent with BF₃ coordination, while ¹¹B NMR shows peaks near 0 ppm. It's stable under GC-MS or HPLC conditions, aiding quality verification.
Storage and Stability
Store BF₃·CH₃CN under dry, inert conditions like nitrogen or argon, in tightly sealed containers away from moisture—think of it as keeping bread in a sealed bag to prevent staleness. Recommended temperature: 2-8°C in an explosion-proof refrigerator. Use glass bottles, ampoules, or compatible plastics; avoid glass if reactive. Shelf life is extended in cool, dry environments.
Summary
Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex (CAS 420-16-6) features a liquid state, miscibility with organics, and strong Lewis acidity, balanced by improved stability over pure BF₃. Its reactivity with moisture underscores the need for careful handling, while properties like density and vapor pressure aid practical use. Understanding the physical and chemical properties of Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex (CAS 420-16-6) is essential for its safe handling and effective application in organic synthesis and catalysis.
Related Articles
Looking for a reliable bulk supplier of Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex?
Aure Chemical provides Premium Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex CAS 420-16-6.
View our Boron Trifluoride Acetonitrile Complex product page
