Triflic Acid and Triflate Chemistry: Properties, Reagents, and Industrial Applications
What Is Triflic Acid and Triflate Chemistry?
Triflic acid and its derivatives represent a class of compounds central to advanced chemical processes across various sectors. These materials facilitate transformations that require strong acidity or specific leaving group characteristics, enabling precise control in synthetic pathways. The chemistry encompasses acids, anhydrides, and salts, each tailored to distinct roles in research and industrial settings.
Definition of Triflic Acid (Trifluoromethanesulfonic Acid)
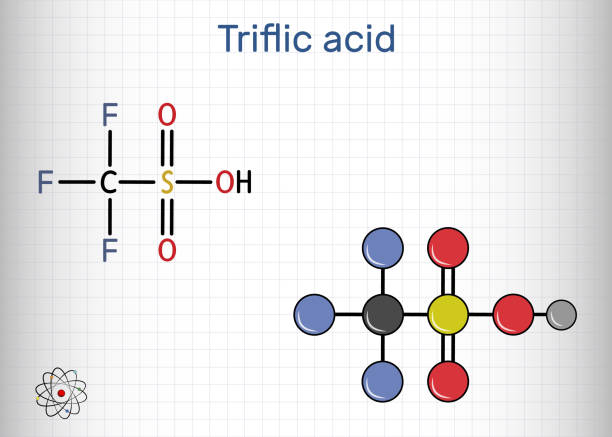 Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, commonly known as triflic acid, stands out as a potent sulfonic acid derivative. Its structure features a trifluoromethyl group attached to a sulfonyl moiety, conferring exceptional acidity. This compound appears as a colorless, viscous liquid with high hygroscopicity, readily absorbing moisture from the environment. In practice, triflic acid serves as a versatile reagent in scenarios demanding robust protonation capabilities, distinguishing it from weaker acids like sulfuric or hydrochloric varieties. Its utility spans from laboratory-scale experiments to large-scale manufacturing, where it acts as a catalyst or activator without introducing unwanted side reactions.
Trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, commonly known as triflic acid, stands out as a potent sulfonic acid derivative. Its structure features a trifluoromethyl group attached to a sulfonyl moiety, conferring exceptional acidity. This compound appears as a colorless, viscous liquid with high hygroscopicity, readily absorbing moisture from the environment. In practice, triflic acid serves as a versatile reagent in scenarios demanding robust protonation capabilities, distinguishing it from weaker acids like sulfuric or hydrochloric varieties. Its utility spans from laboratory-scale experiments to large-scale manufacturing, where it acts as a catalyst or activator without introducing unwanted side reactions.
Triflates and Triflimides: A Broader Chemical Family
Triflates refer to esters or salts derived from triflic acid, characterized by the trifluoromethanesulfonate anion. These entities exhibit excellent leaving group properties due to the stability of the anion, making them indispensable in substitution reactions. Triflimides, on the other hand, involve the bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide anion, often abbreviated as TFSI. This family extends the scope of triflate chemistry by providing anions with unique solvation behaviors, particularly in ionic liquids and electrolyte systems. Together, triflates and triflimides broaden the applicability of triflic acid-derived materials, offering options for both organic transformations and specialized material formulations.
Key Physicochemical Properties of Triflic Acid and Triflates
The distinctive attributes of triflic acid and its derivatives underpin their widespread adoption in chemical methodologies. These properties include extreme acidity, resistance to decomposition, and minimal interference in reaction environments, which collectively enhance their performance across diverse applications.
Superacidity and Non-Oxidizing Nature
Triflic acid ranks among the strongest known Brønsted acids, with a Hammett acidity function value indicating superior proton-donating ability compared to many mineral acids. This superacidity allows it to protonate substrates that remain inert under milder conditions, facilitating reactions in non-aqueous media. Importantly, triflic acid lacks oxidizing potential, unlike some strong acids that can induce redox side effects. This non-oxidizing characteristic ensures clean reaction profiles, preserving the integrity of sensitive functional groups. Triflates inherit this stability, functioning effectively as leaving groups without promoting unintended oxidations.
Thermal Stability and Weakly Coordinating Anions
High thermal resilience defines triflic acid and triflates, enabling their use in elevated-temperature processes without significant degradation. The trifluoromethanesulfonate anion demonstrates weak coordination to metal centers, a trait that minimizes solvation effects and enhances catalytic efficiency. In contrast to more nucleophilic anions, this weak coordination prevents catalyst poisoning and supports recyclability in certain systems. Triflimides amplify this property, with the TFSI anion exhibiting even lower nucleophilicity, ideal for environments requiring unobtrusive counterions.
Major Application Areas of Triflic Acid and Triflate Chemistry
Triflic acid and triflates find utility in several critical domains, from synthetic chemistry to advanced materials. These areas leverage the compounds' unique properties to address challenges in efficiency, selectivity, and scalability.
Triflic Acid as a Superacid and Activation Reagent
Triflic acid excels in roles requiring intense protonation, such as activating carbonyl compounds or facilitating rearrangements. Its application extends to esterification and other condensation reactions, where it promotes bond formation under mild conditions. Researchers in organic synthesis value its ability to handle recalcitrant substrates, while industrial processes benefit from its catalytic turnover. For deeper insights into these uses, refer to triflic acid as a superacid and activation reagent in organic synthesis.
Triflation Reagents in Organic Synthesis
Triflation involves introducing the trifluoromethanesulfonyl group, often via triflic anhydride or related reagents. This process converts alcohols or amines into reactive intermediates suitable for nucleophilic substitutions or cross-couplings. The resulting triflates serve as versatile handles in constructing complex molecular architectures, particularly in pharmaceutical development. Their stability and reactivity balance make them preferable over halides in many contexts. Explore further details in triflation reagents in organic synthesis.
Metal Triflates as Lewis Acid Catalysts
Metal salts incorporating the triflate anion function as effective Lewis acids, coordinating to electron-rich sites to activate substrates. Common examples include scandium, ytterbium, and lanthanum triflates, which catalyze acylation, aldol condensations, and cycloadditions. The water tolerance of these catalysts allows operations in aqueous or protic solvents, expanding their scope beyond anhydrous conditions. Their recyclability adds to their appeal in sustainable processes. Additional information is available in metal triflates as Lewis acid catalysts in organic synthesis.
Triflate and TFSI Salts in Electrochemistry and Materials Science
Triflate salts and TFSI derivatives play pivotal roles in electrochemical systems, serving as electrolytes or ionic liquid components. The TFSI anion's low viscosity and high conductivity enhance ion transport in batteries and supercapacitors. In materials science, these compounds contribute to polymer electrolytes and conductive films, improving device performance. Their chemical inertness ensures longevity in harsh environments. For a comprehensive view, consult TFSI and triflate salts in electrochemistry.
How to Select Triflic Acid and Triflate Reagents for Different Applications
Choosing the appropriate form of triflic acid or triflate requires consideration of reaction specifics, substrate compatibility, and operational constraints. Factors such as reagent purity and form influence outcomes in both research and production settings.
Purity, Water Content, and Handling Considerations
High-purity triflic acid minimizes impurities that could interfere with sensitive reactions, particularly in catalysis. Water content poses a challenge due to the compound's hygroscopicity, potentially diluting acidity or promoting hydrolysis. Anhydrous grades suit moisture-sensitive applications, while controlled hydration may be tolerable in others. Handling demands inert atmospheres to prevent degradation, with storage in sealed containers recommended to maintain integrity. Procurement managers should evaluate supplier quality controls to ensure consistency across batches.
Choosing Between Triflic Acid, Triflic Anhydride, and Triflates
Triflic acid suits direct protonation tasks, offering simplicity in addition to substrates. Triflic anhydride provides a means for triflation without generating water, ideal for dehydrative couplings. Triflates, as preformed salts or esters, offer convenience in catalytic or stoichiometric roles, with metal variants tailored for Lewis acidity. Selection hinges on the desired reactivity profile: acid for Brønsted catalysis, anhydride for functional group installation, and salts for coordination-driven processes. Balancing cost, availability, and reaction efficiency guides the decision.
Safety, Handling, and Regulatory Considerations

Proper management of triflic acid and triflates mitigates risks associated with their corrosive nature and reactivity. Adherence to established protocols ensures safe integration into workflows.
General Safety and Storage Principles
Triflic acid's corrosiveness necessitates personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and acid-resistant clothing. Ventilation systems prevent vapor accumulation, while spill kits with neutralizing agents address accidents. Storage involves cool, dry conditions in compatible containers, away from bases or metals to avoid exothermic reactions. Triflates require similar precautions, with dust control for solid forms. Emergency procedures include immediate rinsing with water and medical attention for exposures.
Documentation and Compliance Overview
Regulatory frameworks govern the use of triflic acid and derivatives, emphasizing hazard communication through safety data sheets. Compliance involves labeling, training, and waste disposal per environmental standards. International transport regulations classify these materials as corrosives, requiring appropriate packaging. Documentation tracks usage and incidents, supporting audits and continuous improvement in safety practices.
From Chemistry Overview to Industrial Reagents
The transition from fundamental properties to practical reagents underscores the versatility of triflic acid and triflate systems. These compounds bridge laboratory innovations with industrial scalability, enabling advancements in synthesis, catalysis, and materials. As research evolves, their roles continue to expand, addressing emerging needs in efficient chemical transformations. This overview positions triflic acid and triflates as essential tools for chemists and engineers pursuing precision and performance in their endeavors.

