Monoethylamine in Pesticide & Herbicide Production
In the world of modern agriculture, protecting crops from pests, weeds, and diseases is essential for ensuring food security an d high yields. Behind many effective pesticides and herbicides lies a key chemical building block: monoethylamine (MEA). This versatile compound plays a crucial role in synthesizing some of the most widely used agrochemicals, helping farmers manage threats efficiently while aiming for sustainable practices.
d high yields. Behind many effective pesticides and herbicides lies a key chemical building block: monoethylamine (MEA). This versatile compound plays a crucial role in synthesizing some of the most widely used agrochemicals, helping farmers manage threats efficiently while aiming for sustainable practices.
Monoethylamine, often abbreviated as MEA, is a simple yet powerful organic compound that's colorless, has a strong ammonia-like smell, and is highly reactive. Think of it as a "social butterfly" in chemistry – it's eager to bond with other molecules, making it indispensable in creating complex agrochemicals.
Amines like MEA are critical in agrochemical synthesis because they act as intermediates, helping build the molecular structures that target pests or weeds specifically without harming crops excessively. In modern pesticide and herbicide production, MEA contributes to formulations that are more effective, stable, and sometimes even more environmentally considerate.
This complete guide is designed for agrochemical formulators, procurement specialists, R&D professionals, and manufacturers who want to understand MEA's role deeply – from its chemistry to practical applications, safety, and future trends.
What Is Monoethylamine?
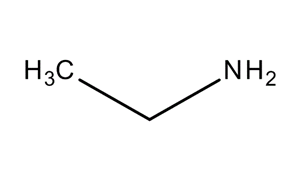
Monoethylamine (chemical name: ethanamine, CAS number 75-04-7) has the molecular formula C₂H₅NH₂. Imagine it as ammonia (NH₃) where one hydrogen is replaced by an ethyl group (C₂H₅) – like upgrading a basic bicycle to one with an extra gear for more versatility.
Its key characteristics include strong basicity (it readily accepts protons, like a sponge soaking up acid) and nucleophilicity (it loves attacking electron-deficient sites in other molecules). Industrially, MEA is available in grades suited for large-scale use, typically as aqueous solutions (e.g., 70%), versus high-purity reagent-grade for lab work.
Why Monoethylamine Is Important in Agrochemical Manufacturing
MEA's reactivity shines when it bonds with acids, alkyl halides, or carbonyl compounds – think of it as a precise Lego piece that snaps into place to form larger structures. It serves as an intermediate (building block), neutralizing agent (balancing pH), or salt-forming amine (improving solubility).
Compared to methylamine (smaller, more volatile) or diethylamine (bulkier, less selective), MEA strikes a balance: reactive enough for efficient synthesis but manageable for industrial scales.

Applications of Monoethylamine in Pesticide Production
Insecticide Synthesis
While MEA is more prominent in herbicides, it contributes to certain intermediates in organophosphate or carbamate insecticides through amine substitution reactions, enhancing efficacy and stability.
Fungicide Manufacturing
MEA aids in building heterocyclic rings for systemic fungicides that protect plants from the inside out.
Plant Growth Regulators & Specialty Agrochemicals
It helps form quaternary ammonium compounds for niche, high-value products.
Role of Monoethylamine in Herbicide Production
MEA truly excels here: it's a precursor for triazine herbicides like atrazine, simazine, and cyanazine. These disrupt photosynthesis in weeds, acting like cutting off a plant's food supply.
Additionally, MEA forms amine salts with acidic herbicides, dramatically improving water solubility – similar to how adding salt to ice lowers its melting point, making the herbicide easier to spray and absorb.
Advantages of MEA salts over sodium or potassium versions include better plant uptake and reduced environmental persistence in some cases.
Key Advantages of Monoethylamine for Agrochemical Formulators
High reactivity → Predictable, efficient reactions (like a reliable recipe).
Improved performance → Better solubility and stability in final products.
Cost efficiency → Scalable production from ethanol and ammonia.
Compatibility → Suits large-scale synthesis without exotic equipment.
Safety, Handling, and Regulatory Considerations
Safety Characteristics
MEA is highly flammable (flash point below 0°F) and volatile, like gasoline – keep away from sparks. It's also corrosive, irritating skin, eyes, and lungs, much like strong household bleach.
Storage and Transportation
Store in cool, ventilated areas; use steel drums or ISO tanks. UN classification: flammable corrosive liquid/gas.
Regulatory Status
Registered under REACH (EU) and listed on TSCA inventory (US), with compliance required for agrochemical uses.
Quality Specifications for Agrochemical Use
Typical purity: >99% for intermediates; low water/impurities; consistent batches with COA for traceability.
Monoethylamine Supply Considerations
Produced globally from ethanol/ammonia; reliable suppliers ensure steady logistics, MOQs, and lead times.
Alternatives to Monoethylamine
Methylamine, diethylamine, or ammonia derivatives – but substitution may alter efficacy or cost; not always feasible for specific herbicides like atrazine.
Future Outlook: Monoethylamine in Sustainable Agrochemicals
With pressure for greener formulations, MEA's role in precise, lower-volume products supports reduced environmental impact while meeting regulatory demands.
Monoethylamine is a cornerstone in pesticide and herbicide production, enabling effective, scalable agrochemicals that protect crops worldwide. Its reactivity, versatility, and advantages make it indispensable for formulators seeking performance and reliability.
For technical specifications, sourcing advice, or expert consultation, reach out to trusted suppliers or specialists in the field. Stay ahead in agrochemical innovation with informed choices.

