Applications of TMSOTf in Pharmaceutical and Fine Chemical Synthesis
If you've ever wondered how tiny molecules can supercharge the creation of life-saving drugs or luxurious scents, meet TMSOTf – a powerhouse reagent that's like the Swiss Army knife of organic synthesis. In this post, we'll explore its properties, applications, and why it's a go-to in labs and factories. Whether you're a student, researcher, or just curious, let's break it down with some everyday analogies to keep things relatable.
Introduction
Trimethylsilyl Trifluoromethanesulfonate (TMSOTf, CAS 27607-77-8) is a highly reactive organosilicon reagent that acts as both a strong silylating agent and an activator. Imagine it as a molecular "energizer" – it's moisture-sensitive and a potent Lewis acid, meaning it loves to grab electrons like a magnet attracting iron filings. This makes it perfect for creating electrophilic intermediates under gentle conditions, without the harshness that could damage delicate compounds.
In organic and industrial chemistry, TMSOTf shines as a catalyst, promoter for acylation reactions, and former of protective groups. Its widespread adoption in pharmaceutical and fine chemical manufacturing comes from its ability to enable precise, efficient syntheses – think of it as the secret ingredient that helps turn raw materials into active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or specialty products with minimal fuss.
Chemical Nature and Reactivity of TMSOTf
At its core, TMSOTf has the chemical formula (CH₃)₃SiOSO₂CF₃. Its reactivity stems from the polarized Si–O–S bond, making it a strong Lewis acid – like a thirsty sponge soaking up electron pairs from other molecules.
Compared to other silylating agents like TMSCl (trimethylsilyl chloride) or TMSI (trimethylsilyl iodide), TMSOTf is stronger and milder, allowing faster reactions without needing extreme conditions. It's especially great at activating carbonyl groups, ethers, and halides, or generating carbocations – essentially, it kickstarts reactions by creating positively charged "hot spots" that attract nucleophiles.
For example, in a basic silylation: R–OH + TMSOTf → R–OTMS + HOTf. Here, it's like slapping a temporary sticker on an alcohol group to protect it during other chemical tweaks.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Synthesis
This is where TMSOTf really flexes its muscles, playing a starring role in crafting complex drugs.
Silylation of Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids
TMSOTf quickly converts hydroxyl (-OH) and carboxyl (-COOH) groups into trimethylsilyl derivatives, acting like a protective wrapper on fragile items during shipping. This is crucial for multi-step API synthesis, where you don’t want certain parts reacting prematurely.
Reaction scheme for silylation of alcohols using TMSOTf
The reaction zips along at low temperatures with mild bases like pyridine or lutidine, making it ideal for sensitive molecules in steroids or nucleosides.
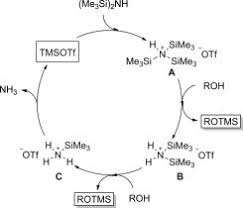
Glycosylation and Nucleoside Synthesis
In glycosylation, TMSOTf activates protected sugars (like those with acetyl or benzyl groups) to form O- or N-glycosidic bonds – think of it as linking sugar “Lego blocks” to build intricate carbohydrate structures. It creates oxocarbenium intermediates gently, ensuring high yields and the right stereochemistry (3D arrangement).
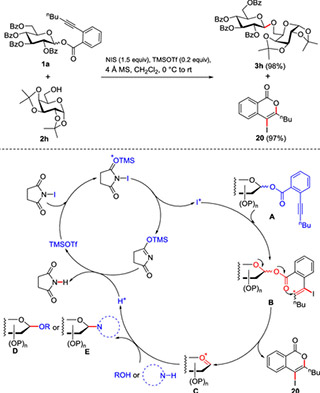
Glycosylation reaction promoted by TMSOTf
This is key for antiviral drugs and nucleotide analogs, such as coupling silylated nucleobases with sugar donors.
Friedel–Crafts and Acylation Reactions
As a non-metallic Lewis acid, TMSOTf catalyzes acylation, alkylation, and cyclization without leaving metal traces – perfect for GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) in pharma, where purity is paramount. It’s like a clean chef who doesn’t contaminate the dish.
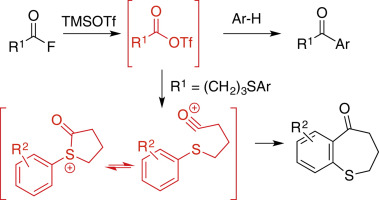
Friedel–Crafts and acylation reactions catalyzed by TMSOTf
Examples include intramolecular cyclizations or aromatic substitutions, building ring structures in drug scaffolds.
Carbonyl Activation and Rearrangement Reactions
TMSOTf wakes up carbonyl groups to form carbocations or enol silanes, facilitating reactions like Baeyer–Villiger oxidations (expanding rings by inserting oxygen) or Beckmann rearrangements (swapping atoms in amides). Compared to harsher agents like AlCl₃ or BF₃·Et₂O, it offers better selectivity and fewer side products – like choosing a precision tool over a sledgehammer.
Applications in Fine and Specialty Chemicals
Beyond pharma, TMSOTf thrives in creating high-value niche products.
Silylation in Flavor and Fragrance Intermediates
It enables mild esterifications and etherifications for delicate compounds, reducing unwanted color or breakdown – imagine gently blending ingredients for a perfume without scorching them, unlike stronger acid catalysts.
Catalyst for Organic Transformations
TMSOTf promotes Diels–Alder cycloadditions (fusing rings like snapping puzzle pieces), Mukaiyama aldol reactions (building carbon chains), and nitrile activations. It's compatible with silicon- and fluorine-based materials in specialty polymers.
Typical Reaction Conditions
Here's a handy guide for running TMSOTf reactions safely and effectively:
| Parameter | Typical Range |
| Solvent | Dichloromethane, acetonitrile, or toluene |
| Temperature | −78 °C to room temperature |
| Catalyst loading | 1–10 mol% |
| Atmosphere | Dry nitrogen or argon |
| Work-up | Quench with aqueous NaHCO₃, extract, dry, and purify |
Quick safety note: TMSOTf reacts violently with moisture, forming triflic acid – handle it like a firecracker around water!
Advantages over Other Silylating Agents
Why pick TMSOTf? Check this comparison:
| Reagent | Strength | Reaction Rate | Metal-free | Comments |
| TMSCl | Moderate | Slow | ✅ | Requires strong base |
| TMSI | Very strong | Fast | ❌ | Generates iodine waste |
| TMSOTf | Strongest | Very fast | ✅ | Mild conditions, high selectivity |
Handling and Safety Considerations
TMSOTf is extremely moisture-sensitive, so always handle it under inert gas to avoid explosive hydrolysis into corrosive triflic acid. Store in amber-sealed bottles at ≤5 °C under nitrogen, and use PTFE-lined equipment with full PPE (gloves, goggles) – treat it like handling hot oil in the kitchen.
Outlook and Future Developments
With the push for green chemistry and metal-free processes, TMSOTf's star is rising. Emerging uses in fluorinated pharma intermediates and silicon materials promise more. Ongoing tweaks to its synthesis and stability could scale it up for bigger industrial wins.
Trimethylsilyl Triflate (TMSOTf) stands as one of the most versatile and powerful reagents in modern synthesis. Its dual role as a silylating and catalytic agent enables numerous key transformations in the manufacture of APIs and fine chemicals, combining efficiency, selectivity, and metal-free processing advantages.




